Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
Fermentation
A process that allows glycolysis to continue producing ATP when oxygen is not available by regenerating NAD+.
What is the main purpose of fermentation?
To regenerate NAD+ so glycolysis can continue producing ATP in the absence of oxygen.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
A type of fermentation where pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid, regenerating NAD+.
What happens to pyruvate in lactic acid fermentation?
It is reduced to lactic acid.
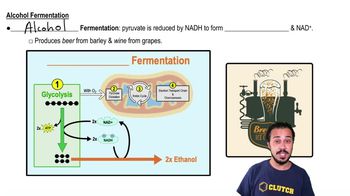
Alcohol Fermentation
A type of fermentation where pyruvate is reduced to ethanol, regenerating NAD+.
What is produced in alcohol fermentation?
Ethanol and NAD+.
Anaerobic Respiration
A process that uses alternative electron acceptors like nitrate or sulfate to generate ATP without oxygen.
What are some alternative electron acceptors in anaerobic respiration?
Nitrate (NO3-) and sulfate (SO4 2-).
NAD+
An electron carrier that is regenerated during fermentation to allow glycolysis to continue.
Why is NAD+ important in fermentation?
It is needed to keep glycolysis running by accepting electrons.
Glycolysis
The first step of cellular respiration that breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
How many ATP molecules are produced in glycolysis?
2 ATP molecules.
Pyruvate
The end product of glycolysis that can be further processed in fermentation or cellular respiration.
What happens to pyruvate in the absence of oxygen?
It undergoes fermentation to form either lactic acid or ethanol.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of protein complexes that transfer electrons to generate a large amount of ATP, requiring oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
What happens to the electron transport chain without oxygen?
It gets backed up, stopping ATP production and increasing NADH levels.
ATP
A molecule that stores and transfers energy within cells.
How does fermentation affect ATP production?
It allows a small amount of ATP to be produced by glycolysis in the absence of oxygen.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor, while anaerobic respiration uses alternative acceptors like nitrate or sulfate.
NADH
An electron carrier that donates electrons to the electron transport chain.
What role does NADH play in fermentation?
It donates electrons to pyruvate, regenerating NAD+.
Chemiosmosis
The process of generating ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme.
Why can't multicellular organisms rely solely on fermentation?
Fermentation produces too little ATP to meet the energy needs of multicellular organisms.
Krebs Cycle
A series of reactions that produce electron carriers for the electron transport chain, occurring only in the presence of oxygen.
What is the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration?
Oxygen.
Sulfate (SO4 2-)
An alternative electron acceptor used in anaerobic respiration.
What is the significance of fermentation in muscle cells?
It allows muscle cells to produce ATP during intense exercise when oxygen is low.
Nitrate (NO3-)
An alternative electron acceptor used in anaerobic respiration.
What is the main difference between lactic acid and alcohol fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid, while alcohol fermentation produces ethanol.