Evidence of Evolution exam Flashcards
 Back
BackEvidence of Evolution exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
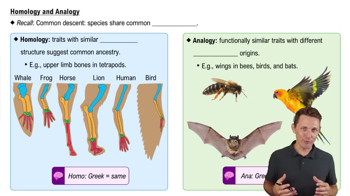
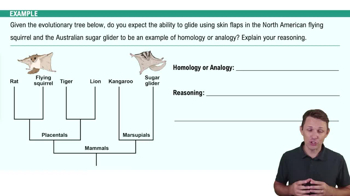
- HomologyTraits with similar underlying structures suggesting common ancestry.
- What are vestigial structures?Traits that have lost most or all of their ancestral function.
- Embryologic homologySimilarities in early development stages among different species.
- What is molecular homology?DNA and protein sequence similarities in related organisms.
- FossilsRemains of organisms from the past found in layers of rock or sediment.
- What do deeper geologic layers indicate?Older layers with organisms different from those seen today.
- TetrapodsOrganisms that live on land and have a backbone.
- What is an example of a vestigial structure in humans?Goosebumps, which are remnants of fur-raising mechanisms.
- AnalogyFunctionally similar traits with different evolutionary origins.
- What is the significance of the humerus in tetrapods?A common bone structure indicating shared ancestry.
- Pharyngeal archesEmbryonic structures that develop into different but related structures in adults.
- What do molecular homologies help construct?Evolutionary trees based on DNA and protein similarities.
- Descent with modificationThe process by which traits are passed on and modified over generations.
- What evidence do fossils provide?Both broad patterns and specific transitions in evolution.
- Pelvic girdle in snakesA vestigial structure indicating legged ancestors.
- What is an example of embryologic homology?Pharyngeal arches and post-anal tails in vertebrate embryos.
- Intermediate leg structures in whale evolutionFossil evidence showing the transition from land-dwelling to aquatic life.
- What does the presence of a vestigial pelvis in modern whales indicate?Ancestral connection to land-dwelling mammals.
- DarudinAn ancient whale with vestigial legs, showing evolutionary transition.
- What is the significance of Rodicetus in whale evolution?A transitional fossil with swimming legs, indicating adaptation to aquatic life.
- IndohyasAn early ancestor of whales with legs used for walking on land.
- What do geologic layers demonstrate?The timeline of Earth's history and evolutionary changes.
- Why are wings in bees, birds, and bats considered analogous?They have different evolutionary origins despite similar functions.
- What does the term 'terrestrial' mean?Living on land.
- How do fossils demonstrate specific evolutionary histories?By showing transitional forms and adaptations over time.
- What is the role of sediment in fossil formation?Traps and preserves organisms, forming layers over time.
- Why are embryonic traits stable through evolutionary time?Early developmental changes can cause significant downstream effects.
- What is the importance of homology in evolutionary biology?It helps understand evolutionary relationships and common ancestry.
- What does the term 'descent with modification' imply?Evolutionary changes occur through small modifications over generations.