Back
BackEukaryotic RNA Processing and Splicing definitions
Terms in this set (16)
Eukaryotic RNA Processing
The process in eukaryotes where pre-mRNA undergoes modifications, including splicing, 5' capping, and polyadenylation, to become mature mRNA ready for translation.
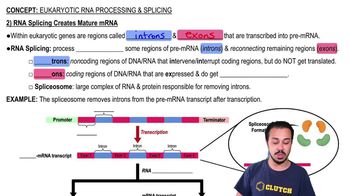
Splicing
The process of removing introns and joining exons in pre-mRNA to produce mature mRNA ready for translation in eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic mRNA
mRNA in prokaryotes is directly translated into proteins without requiring post-transcriptional modifications like capping, polyadenylation, or splicing, unlike eukaryotic mRNA.
Transcription Termination
The process where RNA polymerase stops RNA synthesis and releases the newly made RNA transcript and the DNA template.
Premature mRNA
The initial RNA transcript in eukaryotes that requires processing and splicing to become mature mRNA ready for translation.
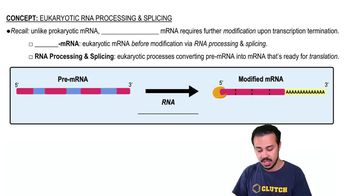
Pre mRNA
The initial RNA transcript in eukaryotes, containing both exons and introns, which requires processing and splicing to become mature mRNA ready for translation.
RNA Processing
Modification of pre-mRNA in eukaryotes, involving capping, polyadenylation, and splicing, to produce mature mRNA ready for translation.
Translation
The process where mature mRNA is decoded by ribosomes to synthesize a specific protein, using tRNA to match amino acids to the mRNA codons.
mRNA Poly A Tail
A sequence of adenine nucleotides added to the 3' end of eukaryotic mRNA to protect it from degradation and assist in translation.
3 Prime End
The end of an mRNA strand where a poly-A tail is added during RNA processing to protect the mRNA from degradation and aid in translation.
5 Prime Cap
A modified guanine nucleotide added to the 5' end of eukaryotic pre-mRNA, protecting it from degradation and aiding in ribosome binding during translation.
RNA Modification
Post-transcriptional changes in eukaryotic pre-mRNA, including splicing, 5' capping, and 3' polyadenylation, to produce mature mRNA ready for translation.
Gene Products
Molecules synthesized as a result of gene expression, including proteins and functional RNAs, which perform various cellular functions.
Exons
Segments of DNA or RNA that encode parts of the final mature RNA product, such as proteins, and are retained after splicing.
Introns
Noncoding segments of pre-mRNA that are removed during RNA splicing in eukaryotic cells.
Noncoding Portions
Segments of DNA or RNA that do not encode protein sequences and are removed during RNA splicing are known as noncoding portions.