Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (26)
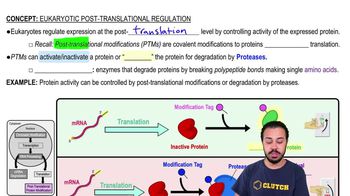
Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs)
Covalent modifications to proteins after translation that can activate or inactivate proteins.
What is the role of proteases in post-translational regulation?
Proteases degrade proteins by breaking polypeptide bonds into amino acids.
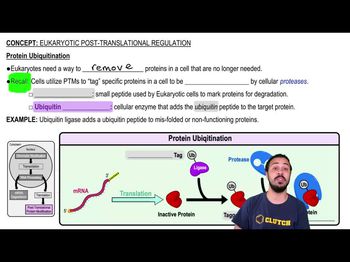
Ubiquitination
A PTM where ubiquitin ligase adds ubiquitin to proteins, marking them for degradation.
What does ubiquitin ligase do?
It adds ubiquitin to target proteins for degradation.
Protease
An enzyme that degrades proteins by breaking polypeptide bonds.
How do PTMs regulate gene expression?
By activating or inactivating proteins, or marking them for degradation.
What happens to proteins tagged with ubiquitin?
They are marked for degradation by proteases.
Gene Expression Regulation
The process of turning genes on or off through mechanisms like PTMs.
What is the outcome of protein degradation?
Proteins are broken down into individual amino acids.
Inactive Protein
A protein that is not functional until it undergoes post-translational modification.
What is the significance of ubiquitination in cellular function?
It helps maintain cellular homeostasis by removing unnecessary or misfolded proteins.
Active Protein
A protein that has been modified post-translationally to become functional.
What does the term 'post' in post-translational modifications refer to?
It refers to modifications that occur after translation.
Ubiquitin
A small peptide used to tag proteins for degradation.
How do proteases contribute to cellular homeostasis?
By degrading unnecessary or misfolded proteins, maintaining protein balance.
Protein Degradation
The process of breaking down proteins into amino acids by proteases.
What is the function of ubiquitin ligase in ubiquitination?
It transfers ubiquitin to target proteins, marking them for degradation.
Misfolded Protein
A protein that has not folded into its correct functional shape and is often targeted for degradation.
What is the result of protein ubiquitination?
The tagged protein is degraded by proteases.
What is the role of PTMs in protein activity?
PTMs can either activate or inactivate proteins.
Amino Acids
The building blocks of proteins, released during protein degradation.
What is the purpose of tagging proteins for degradation?
To remove proteins that are no longer needed or are misfolded.
Protein Activity Control
Regulated by post-translational modifications and degradation by proteases.
What does protein degradation achieve in terms of gene regulation?
It turns off genes by removing their protein products.
Ubiquitin Ligase
An enzyme that adds ubiquitin to proteins, marking them for degradation.
What is the effect of PTMs on gene expression?
PTMs can turn genes on or off by modifying protein activity.