Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (28)
Histone Acetylation
The addition of acetyl groups to histone proteins, loosening chromatin and promoting euchromatin formation, enhancing transcription.
What is the effect of DNA methylation on gene expression?
DNA methylation typically silences genes by adding methyl groups to cytosine residues, blocking transcription.
Euchromatin
A lightly packed region of the genome with high transcriptional activity.
What is the role of histone tails in chromatin modification?
Histone tails can be chemically modified by cellular enzymes, affecting chromatin structure and gene expression.
Heterochromatin
A condensed region of the genome with low transcriptional activity.
What happens during histone deacetylation?
Histone deacetylation removes acetyl groups, resulting in tightly packed chromatin and reduced transcription.
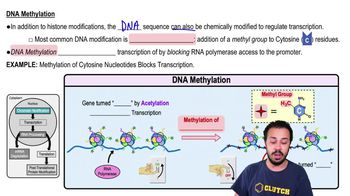
DNA Methylation
The addition of methyl groups to cytosine residues in DNA, typically silencing gene expression.
What is the impact of histone acetylation on chromatin structure?
Histone acetylation loosens chromatin structure, making DNA more accessible for transcription.
RNA Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
What is the primary function of euchromatin?
To allow high transcriptional activity by keeping chromatin loosely packed.
Chromatin
A complex of DNA and histone proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
What is the result of DNA methylation on RNA polymerase activity?
DNA methylation blocks RNA polymerase from accessing the DNA, preventing transcription.
Gene Expression
The process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize functional gene products like proteins.
What is the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin?
Heterochromatin is tightly packed with low transcriptional activity, while euchromatin is loosely packed with high transcriptional activity.
Nucleosome
A structural unit of chromatin, consisting of DNA wrapped around a core of histone proteins.
What does histone acetylation promote?
Histone acetylation promotes euchromatin formation and enhances transcription.
Cytosine Methylation
The addition of a methyl group to cytosine residues in DNA, often leading to gene silencing.
What is the role of chromatin modifications in gene regulation?
Chromatin modifications regulate gene expression by altering chromatin structure, affecting the accessibility of DNA to transcription machinery.
What is the effect of histone deacetylation on chromatin?
Histone deacetylation results in tightly packed chromatin, reducing transcriptional activity.
Acetyl Group
A functional group with the chemical formula -COCH3, added to histones during acetylation.
What is the primary function of heterochromatin?
To reduce transcriptional activity by keeping chromatin tightly packed.
Gene Silencing
The process by which a gene's expression is inhibited, often through DNA methylation.
What is the role of histone modifications in chromatin structure?
Histone modifications, such as acetylation and deacetylation, alter chromatin structure and regulate gene expression.
Chromatin Modifications
Chemical changes to histones or DNA that affect chromatin structure and gene expression.
What is the impact of DNA methylation on gene transcription?
DNA methylation typically silences gene transcription by blocking RNA polymerase access.
Histone Proteins
Proteins around which DNA is coiled in nucleosomes, playing a key role in chromatin structure and gene regulation.
What is the function of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications
Changes to chromatin structure, such as histone acetylation and DNA methylation, that regulate gene expression.