Enzyme Binding Factors exam Flashcards
 Back
BackEnzyme Binding Factors exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
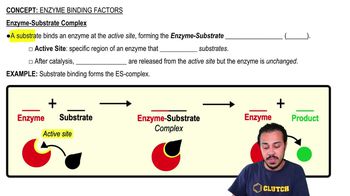
- Active SiteA specific region of an enzyme where the substrate binds.
- What is the enzyme-substrate complex?It is the complex formed when a substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme, abbreviated as ES.
- CofactorsNon-protein substances required by some enzymes for catalysis.
- What happens to the enzyme after catalysis?The enzyme remains unchanged and can catalyze further reactions.
- CoenzymesOrganic molecule cofactors derived from vitamins.
- What role do cofactors play in enzyme activity?They assist in catalysis, often by enhancing substrate binding.
- EnzymeA protein that catalyzes chemical reactions without being consumed.
- What is the abbreviation for the enzyme-substrate complex?ES
- Metal IonsA type of cofactor that is not made of amino acids.
- What is the role of the active site in an enzyme?It binds the substrate to form the enzyme-substrate complex.
- SubstrateThe reactant that an enzyme acts upon.
- What is a coenzyme?A specific type of cofactor that is an organic molecule.
- ProductsThe substances formed from the substrate after catalysis.
- How do cofactors assist enzymes?By binding to the active site and making it better suited for the substrate.
- Enzyme CatalysisThe process by which an enzyme converts substrates into products.
- What is the function of coenzymes?They enhance substrate binding and ensure effective enzyme activity.
- Non-protein SubstancesCofactors required by some enzymes for catalysis.
- What happens to cofactors during the reaction?They are not consumed and remain unchanged.
- Metabolic PathwaysSeries of chemical reactions in a cell, facilitated by enzymes.
- What is the significance of the enzyme remaining unchanged?It allows the enzyme to catalyze multiple reactions repeatedly.
- VitaminsNutrient sources from which coenzymes are derived.
- What is the abbreviation for products in enzyme reactions?P
- Enzyme-Substrate Complex (ES)The intermediate formed when a substrate binds to an enzyme's active site.
- How do metal ions function as cofactors?They assist in enzyme catalysis without being part of the protein structure.
- CatalysisThe acceleration of a chemical reaction by a catalyst.
- What is the role of the active site in enzyme catalysis?It is where the substrate binds and the reaction is facilitated.
- Enzyme FunctionalityThe ability of an enzyme to catalyze reactions, often influenced by cofactors.
- What are the products of enzyme catalysis?The substances formed from the substrate, abbreviated as P.
- Substrate BindingThe process of a substrate attaching to the enzyme's active site.