Ecdysozoans definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackEcdysozoans definitions
1/11
Terms in this set (11)
- EcdysozoansProtostomes that grow by periodically shedding their tough outer cuticle, which can form an exoskeleton; includes arthropods and nematodes.
- ArthropodsOrganisms with segmented bodies, exoskeletons made of chitin, and jointed appendages. They grow by molting their exoskeleton and have diverse forms due to variations in Hox genes.
- ChitinA tough, flexible polysaccharide forming the primary component of arthropod exoskeletons and fungal cell walls, providing structural support and protection.
- Calcium CarbonateA compound that reinforces crustacean exoskeletons, providing structural strength and protection.
- TagmataBody segments in arthropods specialized for different functions, such as the head, thorax, and abdomen in insects.
- Hox GenesGenes that regulate the development and differentiation of body segments, enabling diverse anatomical structures like wings, legs, and antennae in organisms, crucial for evolutionary adaptability.
- HemolymphA fluid in arthropods' main body cavity that functions like blood, directly bathing organs for gas exchange in their open circulatory system.
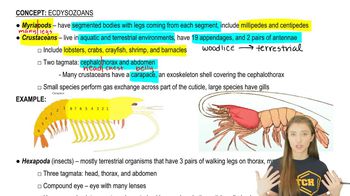
- MyriapodsInvertebrate arthropods with elongated, segmented bodies and numerous legs, including centipedes and millipedes, known for their many-legged appearance and diverse species.
- CrustaceansAquatic and terrestrial arthropods with 19 appendages, 2 pairs of antennae, and a body divided into a cephalothorax and abdomen, often with a calcium carbonate-reinforced exoskeleton.
- CarapaceA hard, protective exoskeleton covering the cephalothorax of crustaceans, providing armor-like defense and requiring shedding for growth.
- HexapodsHexapods are a diverse group of arthropods characterized by three pairs of legs, three body segments (head, thorax, abdomen), and often compound eyes. They include insects and are highly successful in various environments.