Earth's Climate Patterns exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
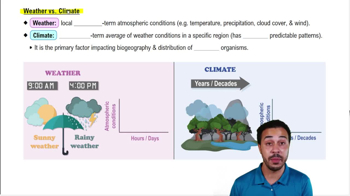
Weather
Local short-term atmospheric conditions, usually measured over hours or days.
Climate
Long-term averages of weather conditions in a specific region, measured over years, decades, or centuries.
What is the primary factor impacting biogeography?
Climate
Latitude
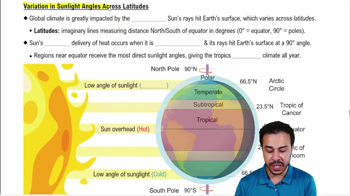
Imaginary lines measuring the distance north or south of the equator in degrees.
What latitude represents the equator?
0 degrees
Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn
Latitudes at 23.5 degrees north and south, defining the tropical region.
What creates the seasons on Earth?
Earth's 23.5-degree axial tilt and its orbit around the sun.
Hadley Cell
A large-scale cycle in global air circulation and precipitation extending from the equator to 30 degrees latitude.
What is the Coriolis Effect?
A phenomenon caused by Earth's rotation that curves the paths of moving objects, including prevailing winds.
High Specific Heat
The property of water that allows it to resist temperature changes, stabilizing nearby land climates.
Rain Shadow
A dry, desert-like area on the leeward side of a mountain range.
What causes a rain shadow?
Mountains forcing air to rise, cool, and lose moisture on the windward side, creating dry conditions on the leeward side.
Prevailing Winds
Winds that blow in consistent directions over long periods, influenced by the Coriolis effect.
What is the role of gyres in climate?
Massive systems of circulating ocean currents that transfer heat from the equator towards the poles.
Photosynthesis
The process that converts solar energy into chemical energy and removes CO2 from the atmosphere, creating a cooling effect.
Transpiration
The evaporation and release of water as gas from plant leaves, forming rain clouds and creating a cooling effect.
What is the impact of deforestation on climate?
Deforested regions reflect more solar energy, creating more heat and less cloud coverage, reducing the cooling effect.
What is the significance of the Arctic and Antarctic Circles?
They define the polar regions at 66.5 degrees latitude north and south.
What happens to air at the equator in the Hadley cell?
It rises, cools, and causes precipitation, creating rainforests.
What is the effect of Earth's axial tilt on sunlight angles?
It causes variability in sunlight angles, creating seasons and influencing climate.
How do mountains affect local ecosystems?
By creating rain shadows and influencing precipitation patterns.
What is the relationship between global air circulation and ocean currents?
Global air circulation impacts ocean surface currents, aligning the direction of prevailing winds with ocean gyres.
What is the impact of water absorbing CO2?
It helps cool the Earth by reducing greenhouse gases but can disrupt aquatic life by forming carbonic acid.
What is the role of forests in climate regulation?
Forests create a cooling effect through photosynthesis and transpiration.
What is the effect of the Coriolis effect on hurricanes?
It causes hurricanes to rotate counterclockwise in the northern hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere.
What is the significance of the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn?
They mark the boundaries of the tropical region, which receives the most direct sunlight.
What is the impact of Earth's spherical shape on climate?
It causes variation in sunlight angles across latitudes, affecting global climate.
What is the effect of high specific heat of water on coastal regions?
It stabilizes temperatures, making coastal regions have more stable climates compared to inland regions.
What is the impact of the Hadley cell on precipitation at 30 degrees latitude?
It creates high surface air pressure, inhibiting rain cloud formation and resulting in deserts.