Digestion exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (27)
Ingestion
The process of taking food into the body through the mouth.
What is the role of the small intestine in digestion?
The small intestine is responsible for nutrient absorption and digestion, aided by its extensive surface area from villi and microvilli.
What is bile and its function?
Bile is a digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder; it emulsifies fats to increase their surface area for digestion.
Hepatic Portal Vein
A blood vessel that transports nutrients from the digestive tract to the liver for detoxification and storage.
What are villi and microvilli?
Villi are small, finger-like projections in the small intestine that increase surface area for absorption. Microvilli are even smaller projections on the villi.
Peristalsis
Wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
What is the function of the large intestine?
The large intestine absorbs water and compacts feces.
Gastric Juice
A mixture of hydrochloric acid, enzymes, and mucus secreted by the stomach to aid in digestion.
What is the role of the liver in digestion?
The liver detoxifies substances, stores nutrients, and produces bile for fat digestion.
Pepsinogen
An inactive enzyme secreted by the stomach that is converted to pepsin in the presence of hydrochloric acid.
What is the function of aquaporins?
Aquaporins are channels that facilitate the efficient passage of water through cell membranes.
Chyme
The semi-fluid mass of partly digested food that is expelled by the stomach into the duodenum.
What are the four stages of food processing in the digestive system?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination.
Ruminants
Mammals with a specialized four-chambered stomach for digesting plant matter, including fermentation.
What is the function of the pancreas in digestion?
The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes and bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid in the small intestine.
What is the role of the appendix?
The appendix houses useful gut bacteria and contains immune-related tissue.
Extracellular Digestion
The breakdown of food outside cells, typically within the lumen of the digestive tract.
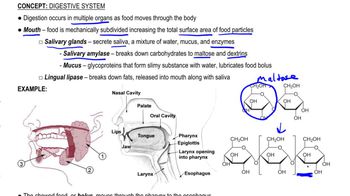
What is the function of salivary amylase?
Salivary amylase is an enzyme in saliva that breaks down carbohydrates into maltose and dextrins.
Micelles
Small aggregates of fat molecules formed during the digestion of fats, aiding in their absorption.
What is the significance of the pyloric sphincter?
The pyloric sphincter regulates the passage of chyme from the stomach to the small intestine.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
A hormone that stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder and digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
What is the role of the colon in the large intestine?
The colon absorbs water and houses beneficial bacteria essential for health.
Lingual Lipase
An enzyme secreted by glands in the tongue that breaks down fats.
What is the function of the sodium-potassium pump in glucose absorption?
The sodium-potassium pump creates a concentration gradient that allows glucose to enter epithelial cells via secondary active transport.
Cloaca
A common cavity in some animals for the excretion of both urine and feces.
What is the function of mucus in the digestive system?
Mucus lubricates food and protects the lining of the digestive tract from harsh substances.
Essential Fatty Acids
Fatty acids that the body cannot synthesize and must be obtained from the diet, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.