Concentration Gradients and Diffusion exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (26)
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration of a substance between two areas.
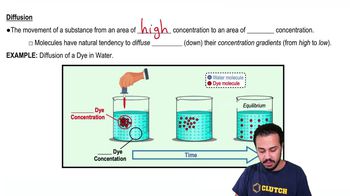
What is diffusion?
The net movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Energy requirement for diffusion
No energy is required for molecules to move down their concentration gradient.
What happens when a molecule moves against its concentration gradient?
It moves from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, requiring energy.
Equilibrium in diffusion
When all particles are evenly distributed, resulting in equal concentration throughout.
What is active transport?
The movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy.
Homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal conditions in an organism.
What is the natural tendency of molecules in diffusion?
To move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What does it mean to move down a concentration gradient?
To move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Energy dynamics in cellular processes
Energy is required for processes like active transport to maintain homeostasis.
What is required for a molecule to move up its concentration gradient?
Energy is required for a molecule to move from low to high concentration.
Metabolic Pathways
Series of chemical reactions in a cell that build and breakdown molecules for cellular processes.
What is the role of energy in active transport?
Energy is used to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
What is the result of diffusion over time?
Molecules spread out evenly, reaching equilibrium.
High concentration
An area where the substance is densely packed.
What does it mean to move with a concentration gradient?
To move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Low concentration
An area where the substance is sparsely distributed.
What is the significance of concentration gradients in biology?
They are crucial for processes like diffusion, active transport, and cellular respiration.
Energy requirement for moving up a concentration gradient
Energy is required to move molecules from low to high concentration.
What is the relationship between concentration gradients and homeostasis?
Maintaining concentration gradients is essential for homeostasis in cells.
Net movement
Overall movement of molecules from high to low concentration in diffusion.
What happens to dye molecules in water over time?
They diffuse from high concentration areas to low concentration areas until evenly distributed.
What is the role of concentration gradients in metabolic pathways?
They drive the movement of substances necessary for metabolic reactions.
Equilibrium
A state where concentrations are equal throughout a system.
What is the difference between moving with and against a concentration gradient?
Moving with the gradient requires no energy, while moving against it requires energy.
Active Transport
Movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy.