Community Dynamics exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (28)
Disturbance
A short-lived event that significantly changes or disrupts the structure and function of a community.
What does the intermediate disturbance hypothesis suggest?
Moderate disturbances foster the highest species diversity by allowing both competitive and less competitive species to coexist.
Ecological Succession
A gradual process of community change over time, which can be primary or secondary.
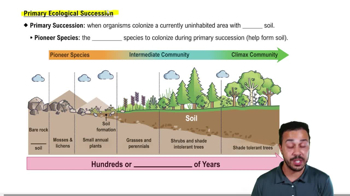
Primary Succession
The colonization of a barren area with no soil, often following volcanic activity or glacial retreat.
What are pioneer species?
The first species to colonize an area during primary succession, often mosses and lichens.
Secondary Succession
The recovery of a community after a disturbance that leaves the soil intact.
Climax Community
The final and most stable stage of ecological succession, though succession still occurs at a reduced rate.
How does secondary succession differ from primary succession?
Secondary succession occurs more rapidly because the soil remains intact, unlike primary succession.
Facilitation
When early arriving species make conditions more favorable for later species.
Tolerance
When existing species do not affect the arrival of later species.
Inhibition
When the presence of certain species inhibits the establishment or regrowth of other species.
What factors influence the impact level of a disturbance?
The type, frequency, and intensity of the disturbance.
Species Diversity
The variety and abundance of different species within a community.
What is the role of pioneer species in soil formation?
Pioneer species help in the slow and gradual process of soil formation.
Intermediate Community
A stage in ecological succession where the community has a mix of species, including grasses, perennials, and shrubs.
What is the significance of soil in secondary succession?
The presence of soil allows for a broader range of pioneer species and speeds up the succession process.
How do disturbances create new opportunities for species?
By changing the availability of resources in the environment.
What is the final stage of ecological succession?
The climax community.
How long can primary succession take?
Several hundred to thousands of years.
What happens to species diversity at low disturbance levels?
Low species diversity due to dominance by the best competitors.
What happens to species diversity at high disturbance levels?
Low species diversity due to only the best adapted species surviving.
What is the impact of moderate disturbance levels on species diversity?
Fosters the highest species diversity.
What is the role of early arriving species in ecological succession?
They can facilitate, tolerate, or inhibit the arrival of later species.
What is the difference between primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession starts with no soil, while secondary succession starts with soil intact.
What is the impact of disturbances on community structure?
Disturbances can reset and accelerate the process of ecological succession.
What is the significance of the climax community in ecological succession?
It is the most stable stage, though ecological succession still occurs at a reduced rate.
How do disturbances affect resource availability?
They change the availability of resources, creating new opportunities for different species.
What is the role of pioneer species in primary succession?
They colonize barren areas and help in soil formation.