Classes of Signaling Receptors exam Flashcards
 Back
BackClasses of Signaling Receptors exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
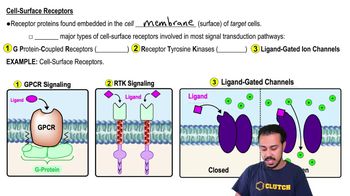
- Cell Surface ReceptorsReceptor proteins found embedded in the cell membrane.
- Intracellular ReceptorsReceptor proteins found within the cell, interacting with small hydrophobic signaling molecules.
- What are the two main classes of signaling receptors?Cell surface receptors and intracellular receptors.
- G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)A type of cell surface receptor that changes conformation when bound to a ligand.
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)A type of cell surface receptor with two domains that phosphorylate tyrosine residues.
- Ligand-Gated Ion ChannelsCell surface receptors that open to allow ions to pass through the membrane upon ligand binding.
- What type of molecules interact with intracellular receptors?Small hydrophobic signaling molecules.
- Signal Transduction PathwaysProcesses by which a cell converts an extracellular signal into a functional response.
- What happens when a ligand binds to a GPCR?The GPCR changes conformation and activates a G protein.
- What is the role of RTKs in cellular signaling?They phosphorylate tyrosine residues on themselves and other proteins to propagate the signal.
- How do ligand-gated ion channels function?They open to allow ions to flow through the membrane when a ligand binds.
- What is the primary location of intracellular receptors?Inside the cell, often in the cytoplasm or nucleus.
- Hydrophobic Signaling MoleculesMolecules that can diffuse across the cell membrane to interact with intracellular receptors.
- What is the main characteristic of cell surface receptors?They are embedded in the cell membrane.
- What triggers the opening of ligand-gated ion channels?Binding of a specific ligand.
- Conformation ChangeA structural change in a receptor protein upon ligand binding.
- What is the function of intracellular receptors?To bind small hydrophobic molecules and trigger a cellular response.
- Cell MembraneThe structure that cell surface receptors are embedded in.
- What are the three major types of cell surface receptors?GPCRs, RTKs, and ligand-gated ion channels.
- CytoplasmThe location within the cell where intracellular receptors are often found.
- What does RTK stand for?Receptor Tyrosine Kinase.
- What does GPCR stand for?G Protein-Coupled Receptor.
- Extracellular FluidThe fluid outside the cell where cell surface receptors interact with ligands.
- What is the role of ligand binding in receptor function?It induces a conformation change in the receptor, initiating a signal transduction pathway.
- Plasma MembraneAnother term for the cell membrane where cell surface receptors are located.
- What type of receptor is involved in most signal transduction pathways?Cell surface receptors.
- What is the primary function of signaling receptors?To detect and respond to specific ligands or signaling molecules.
- What is the difference between cell surface and intracellular receptors?Cell surface receptors are embedded in the cell membrane, while intracellular receptors are found inside the cell.
- What happens after a small hydrophobic molecule binds to an intracellular receptor?It triggers a cascade of events leading to a cellular response.