Chordates exam Flashcards
 Back
BackChordates exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
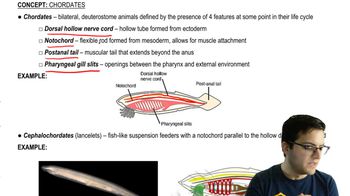
- ChordatesBilateral deuterostome animals with a dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord, postanal tail, and pharyngeal gill slits at some point in their life cycle.
- What are the four key features of chordates?Dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord, postanal tail, and pharyngeal gill slits.
- Dorsal hollow nerve cordA hollow tube formed from the ectoderm, which can develop into the central nervous system.
- What is the function of the notochord?Provides a place for muscle attachment and can develop into the vertebrae in some chordates.
- Postanal tailA tail that extends beyond the anus, present at some stage in all chordates.
- Pharyngeal gill slitsOpenings between the pharynx and the external environment, used for feeding or respiration.
- CephalochordatesPrimitive chordates like lancelets that use pharyngeal gill slits for suspension feeding.
- What are urochordates?Chordates like tunicates that exhibit chordate features only in their larval stage.
- VertebratesChordates with a bony or cartilaginous skeleton, including a vertebrae and cranium.
- What are the three regions of the vertebrate brain?Forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
- GnathostomesJawed vertebrates, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals.
- What is the significance of jaws in vertebrate evolution?Jaws allowed for more efficient feeding and are a major evolutionary milestone.
- Bony endoskeletonAn internal skeleton made mostly of bone, providing support and protection.
- What are ray-finned fish?Bony fish with fins supported by parallel bones and webs of skin, the most diverse group of vertebrates.
- Lobe-finned fishFish with muscular fins that are precursors to the limbs of tetrapods.
- TetrapodsFour-limbed vertebrates that include amphibians, reptiles, and mammals.
- What is a swim bladder?A gas-filled sac in bony fish that helps maintain buoyancy.
- OperculumBony flaps that protect the gills in bony fish.
- AmphibiansEctothermic tetrapods that live both in water and on land, including salamanders, frogs, and apodens.
- What is the function of the closed circulatory system in tetrapods?Delivers sufficient oxygen to limb muscles for life on land.
- Amniotic eggAn egg with specialized membranes that protect the embryo, seen in reptiles and some mammals.
- What are cyclostomes?Jawless fish like hagfish and lampreys, characterized by a circular mouth.
- HagfishJawless fish that secrete slime for defense and have a cartilage skeleton.
- LampreysParasitic jawless fish with a circular mouth filled with teeth, and a cartilage skeleton not made from collagen.
- ChondrichthyansCartilaginous fish like sharks, rays, and skates, with a skeleton made of cartilage.
- What is the lateral line system?A sensory system in fish that detects movements and vibrations in the water.
- What are the three types of reproduction in sharks?Oviparous (egg-laying), ovoviviparous (eggs hatch inside the mother), and viviparous (live birth).
- What is the significance of the coelacanth?A lobe-finned fish once thought extinct, providing insight into the evolution of tetrapods.
- What does ectothermic mean?Organisms that rely on external sources for body heat.