Cell Junctions exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (26)
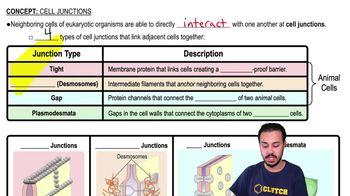
DefineTight Junctions
Membrane proteins that link cells very tightly together, creating a leak-proof barrier.
What is the main function of tight junctions?
To create a leak-proof barrier between adjacent cells.
What are Anchoring Junctions?
Intermediate filaments that anchor neighboring cells together using complex protein structures.
What is another name for anchoring junctions?
Desmosomes.
What are Gap Junctions?
Protein channels that create a gap between two cells, connecting their cytoplasm.
What is the primary role of gap junctions?
To allow the exchange of nutrients and other molecules between neighboring cells.
What are Plasmodesmata?
Gaps in the cell walls of plant cells that connect the cytoplasm of neighboring cells.
Which type of cell junction is found exclusively in plant cells?
Plasmodesmata.
What is the function of plasmodesmata?
To facilitate nutrient transfer between plant cells.
How do tight junctions differ from anchoring junctions?
Tight junctions create a leak-proof barrier, while anchoring junctions allow fluid passage.
What type of junction uses intermediate filaments?
Anchoring junctions (desmosomes).
Which cell junctions are found in animal cells?
Tight junctions, anchoring junctions (desmosomes), and gap junctions.
What do gap junctions and plasmodesmata have in common?
Both create channels that connect the cytoplasm of neighboring cells.
What is the significance of cell junctions in eukaryotic cells?
They are crucial for communication and structural integrity.
Which junction type is responsible for creating a leak-proof barrier?
Tight junctions.
What allows liquids to seep through anchoring junctions?
The junctions are not leak-proof.
How do gap junctions facilitate cellular communication?
By forming protein channels that allow cytoplasmic exchange.
What is the role of protein structures in tight junctions?
To hold cells tightly together, creating a leak-proof barrier.
Which junction type is analogous to gap junctions in plant cells?
Plasmodesmata.
What is the main difference between tight junctions and gap junctions?
Tight junctions create a leak-proof barrier, while gap junctions create channels for cytoplasmic exchange.
How do plasmodesmata benefit plant cells?
By allowing the exchange of nutrients between neighboring cells.
What is the primary function of anchoring junctions?
To anchor neighboring cells together.
Which junction type is essential for tissue organization in animals?
Tight junctions, anchoring junctions, and gap junctions.
What is the structural feature of anchoring junctions?
Intermediate filaments and complex protein structures.
How do tight junctions prevent leakage?
By holding cells very tightly together with membrane proteins.
What is the function of the protein channels in gap junctions?
To connect the cytoplasm of neighboring cells.