Cancer exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (27)
Cancer
A disease characterized by uncontrolled cell division leading to malignant and benign tumors.
Malignant Tumor
A cancerous tumor that can metastasize to other organs.
Benign Tumor
A noncancerous tumor that remains localized and does not metastasize.
What is metastasis?
The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body.
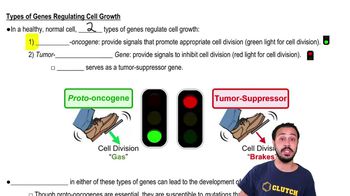
Proto-oncogene
A gene that promotes appropriate cell division, acting like a green light for cell division.
Tumor Suppressor Gene
A gene that inhibits cell division, acting like a red light for cell division.
Oncogene
A mutated proto-oncogene that promotes unrestrained cell growth and cancer development.
What role does p53 play in cell growth?
p53 is a protein that acts as a tumor suppressor gene, inhibiting cell division.
Capsulated Tumor
A tumor surrounded by a capsule of tissue, typically benign and localized.
Non-capsulated Tumor
A tumor not surrounded by a capsule, typically malignant and capable of metastasis.
What is the main difference between malignant and benign tumors?
Malignant tumors are cancerous and can metastasize, while benign tumors are noncancerous and remain localized.
Cell Cycle Regulation
The process by which cells control their growth and division, involving proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.
What happens when proto-oncogenes mutate?
They become oncogenes, leading to unrestrained cell growth and cancer.
What is the function of tumor suppressor genes?
To inhibit cell division and prevent uncontrolled cell growth.
What are the two main types of tumors?
Malignant tumors and benign tumors.
How do malignant tumors affect the body?
They can metastasize to other organs, causing health complications in multiple areas.
What is the role of proto-oncogenes in normal cells?
To promote appropriate cell division.
What is the role of tumor suppressor genes in normal cells?
To inhibit cell division and prevent excessive cell growth.
What is a tumor?
An overgrowth of cells forming an abnormal mass of tissue.
How do benign tumors differ in growth rate compared to malignant tumors?
Benign tumors grow more slowly, while malignant tumors grow very fast.
What is the significance of the capsule in benign tumors?
It contains the tumor cells, preventing them from spreading.
What is the primary danger of malignant tumors?
Their ability to metastasize and affect multiple organs.
What can mutations in tumor suppressor genes lead to?
Uncontrolled cell division and cancer.
What is the main characteristic of cancer cells?
Uncontrolled and unregulated cell division.
How do proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes work together?
Proto-oncogenes promote cell division, while tumor suppressor genes inhibit it, maintaining balance.
What is the effect of oncogenes on cell growth?
They promote unrestrained cell growth, leading to cancer.
What is the role of cell cycle regulation in preventing cancer?
It ensures cells divide appropriately, preventing uncontrolled growth.