C3, C4 & CAM Plants exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
C3 Plants
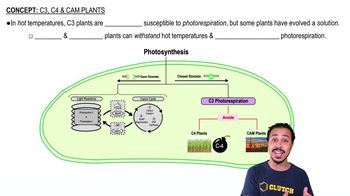
Plants that undergo a single round of carbon fixation in mesophyll cells, making them susceptible to photorespiration.
Why are C3 plants more susceptible to photorespiration?
Because they perform carbon fixation in mesophyll cells, which makes them inefficient in hot climates.
C4 Plants
Plants that perform two rounds of carbon fixation in separate cells, minimizing photorespiration.
What is the first stable molecule produced in C3 plants?
3- Phosphoglycerate (PGA), a 3-carbon intermediate.
CAM Plants
Plants that fix carbon twice at different times, opening stomata at night to conserve water.
How do C4 plants minimize photorespiration?
By performing two rounds of carbon fixation in different cells, mesophyll and bundle sheath cells.
Photorespiration
A process that wastes energy in the form of ATP and NADPH to make CO2, making photosynthesis inefficient.
What is the key adaptation of CAM plants?
They open their stomata at night to fix carbon, reducing water loss.
Mesophyll Cells
Cells where both the light reactions and Calvin cycle occur in C3 plants.
What is the main difference between C3 and C4 plants?
C4 plants perform two rounds of carbon fixation in different cells, while C3 plants do it in one cell.
Bundle Sheath Cells
Cells in C4 plants where the Calvin cycle occurs.
Why do CAM plants open their stomata at night?
To conserve water while still allowing carbon fixation.
Calvin Cycle
The stage of photosynthesis where carbon fixation occurs.
What is the first molecule produced in C4 plants?
Oxaloacetate, a 4-carbon intermediate.
Stomata
Pores on the leaf surface that open and close to regulate gas exchange.
How do C4 plants store carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide is initially fixed as a 4-carbon intermediate (oxaloacetate) in mesophyll cells of C4 plants.
Photorespiration in C3 Plants
Occurs when stomata close in hot temperatures, leading to inefficient photosynthesis.
What is the role of the 4-carbon intermediate in C4 plants?
It supplies additional CO2 when levels get low.
Light Reactions
The stage of photosynthesis that captures light energy to produce ATP and NADPH.
How do CAM plants differ from C4 plants in carbon fixation?
CAM plants fix carbon at different times of the day, while C4 plants do it in different cells.
Carbon Fixation
The process of converting CO2 into organic compounds during photosynthesis.
Why are C4 plants called 'C4'?
Because the first stable molecule produced is a 4-carbon intermediate (Oxaloacetate).
What is the main advantage of CAM plants in arid environments?
They minimize water loss by fixing carbon at night.
ATP and NADPH
Energy molecules produced during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
What happens to stomata in hot temperatures?
They close to prevent dehydration, leading to photorespiration in C3 plants.
C4 Bomb
A mnemonic to remember that C4 plants use two different cells for photosynthesis.
Camel Wearing Pajamas
A mnemonic to remember that CAM plants fix carbon at different times of the day.
What is the significance of the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis?
It is the stage where carbon fixation occurs, producing G3P which can be used to synthesize glucose.
How do C4 plants differ from C3 plants in cell usage?
C4 plants use mesophyll and bundle sheath cells, while C3 plants use only mesophyll cells.