Blood Sugar Homeostasis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (14)
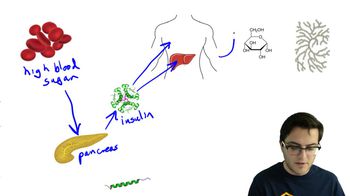
Blood Sugar Homeostasis
The regulation of blood glucose levels through the coordinated actions of insulin and glucagon to maintain a stable internal environment.
Blood Glucose Levels
The concentration of glucose in the bloodstream, regulated by insulin and glucagon, crucial for maintaining energy balance and overall metabolic homeostasis.
Diabetes Mellitus
A chronic condition where blood sugar homeostasis is disrupted due to insufficient insulin production or cellular insensitivity to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas that lowers blood glucose levels by promoting the uptake of glucose into tissues and its storage as glycogen in the liver and muscles.
Glucagon
A hormone from the pancreas that raises blood glucose levels by promoting glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis in the liver.
Pancreas
A gland that produces insulin and glucagon, crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and aiding digestion.
Autoimmune Reaction (Autoimmune disorder)
An immune response where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, such as the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to diseases like type 1 diabetes.
Glycogen
A highly branched polysaccharide stored in the liver and muscles, serving as a primary form of energy storage in animals, and regulated by insulin and glucagon.
Glycogenesis
The process of converting glucose into glycogen for storage in the liver and muscles, primarily in response to insulin.
Gluconeogenesis
The metabolic process of synthesizing glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as amino acids and glycerol, primarily in the liver, to maintain blood sugar levels during fasting.
Hormonal Control
Regulation of physiological processes through hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, to maintain homeostasis, like blood sugar levels, by signaling organs to store or release glucose.
Blood Sugar Levels
The concentration of glucose in the bloodstream, regulated by insulin and glucagon to maintain homeostasis, crucial for energy supply and overall health.
Long Term Store
A reservoir in the liver where glycogen is stored for long-term energy needs, released as glucose when blood sugar levels drop.
Oscillation
The attachment of sugars to body tissues, often due to high blood sugar levels, leading to potential long-term health issues.