Definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (11)
Concentration Gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance between two areas, driving passive movement from high to low concentration or requiring energy to move from low to high concentration.
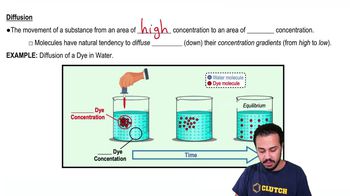
Diffusion
The passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, requiring no energy.
Energy
The capacity to perform work or cause change, often required for molecules to move against their concentration gradient.
Passive Process
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration without energy expenditure, driven by the concentration gradient.
Osmosis
The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration, requiring no energy.
Semipermeable Membrane
A barrier that selectively allows certain molecules or ions to pass through while blocking others, facilitating processes like osmosis and diffusion.
Solute
A substance dissolved in a solvent, forming a solution, and typically present in a lesser amount than the solvent.
Solvent
A substance, typically liquid, that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution, and facilitates the movement of molecules during processes like diffusion and osmosis.
High Concentration
An area where the concentration of a substance is significantly greater compared to another area, often driving diffusion or osmosis processes.
Low Concentration
An area where the concentration of a substance is lower compared to another area, often driving passive transport processes like diffusion.
Passive Function
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration without energy expenditure.