Back
BackBiogeography exam
Terms in this set (27)
Biogeography
The study of how and why organisms are distributed geographically through space and time.
Dispersal
The movement of individuals or their gametes away from their birthplace to other new locations.
What is an endemic species?
A species that is naturally found in only one specific area on earth and nowhere else.
Example of an endemic species
Polar bears in the Arctic.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
An estimate of all the organic matter available as food in a specific region.
What does a high NPP value indicate?
It indicates a region with a lot of organic matter available as food, capable of supporting a lot of life.
Example of a region with high NPP
The Amazon rainforest.
Example of a region with low NPP
The Sahara Desert.
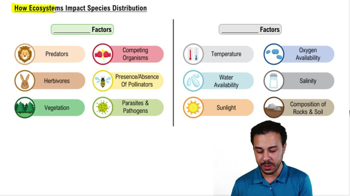
How do biotic factors affect species distribution?
By the presence, absence, or amounts of living factors like predators, herbivores, and vegetation.
How do abiotic factors affect species distribution?
By the presence, absence, or amounts of non-living factors like temperature, water availability, and sunlight.
What is the relationship between NPP and ecosystem health?
Higher NPP values generally indicate healthier ecosystems capable of supporting more life.
Why can't polar bears be found in the South Pole?
Because there is no land mass that directly connects the Arctic to the Antarctic, preventing their dispersal.
What is the significance of dispersal in biogeography?
Dispersal allows species to move to new locations and establish new populations, affecting their geographical distribution.
What role do pollinators play in plant dispersal?
Pollinators help move plant gametes like pollen, aiding in the dispersal of plants.
Arctic Terns
Birds capable of migrating from the North Pole to the South Pole, found throughout the globe.
What is the impact of changing abiotic factors on species distribution?
Changing abiotic factors like temperature or water availability can significantly alter where species can live.
What does NPP stand for?
Net Primary Productivity.
How does NPP affect biomass?
Higher NPP values allow for more biomass, meaning more life can be supported in that region.
What is the main focus of biogeography?
Understanding the geographical distribution of organisms and the factors influencing it.
What are some examples of biotic factors?
Predators, herbivores, vegetation, competing organisms, pollinators, parasites, and pathogens.
What are some examples of abiotic factors?
Temperature, water availability, sunlight, oxygen availability, salinity, and soil composition.
Why is NPP important in ecology?
It serves as an indicator of ecosystem health and the ability to support diverse life forms.
What happens if a species cannot disperse?
It may become endemic, restricted to a specific area.
How does the Amazon rainforest's NPP compare to the Sahara Desert's?
The Amazon rainforest has a high NPP, while the Sahara Desert has a low NPP.
What is the effect of high NPP on an ecosystem?
It supports a diverse and abundant life due to the availability of more organic matter as food.
What is the effect of low NPP on an ecosystem?
It supports less life due to the scarcity of organic matter as food.
How do ecosystems influence species distribution?
Through a combination of biotic and abiotic factors that affect where species can live and thrive.