Back
BackAnimal Development definitions
Terms in this set (25)
Fertilization
The fusion of sperm and egg to form a zygote, initiating development, involving enzymatic reactions to penetrate the egg and prevent polyspermy, typically occurring within 24 hours post-ovulation.
Zygote
The initial cell formed by the fusion of sperm and egg, marking the beginning of embryonic development.
Fallopian Tube
A tube where fertilization occurs, connecting the ovary to the uterus, and facilitating the transport of the egg via cilia.
Cilia
Hair-like structures on cell surfaces that move fluid or cells, aiding in processes like egg transport in fallopian tubes.
Ovulation
The release of a mature egg from the ovary, triggered by the rupture of the follicle, typically occurring midway through the menstrual cycle.
Corpus Luteum
A temporary endocrine structure in the ovary that forms after ovulation, secreting progesterone to maintain the uterine lining for potential pregnancy.
Archosome
A specialized structure at the tip of a sperm cell containing enzymes that facilitate the penetration of the egg's protective layer during fertilization.
Cortical Reaction
A process triggered by sperm entry into the egg, releasing calcium ions that alter the egg's membrane potential, preventing additional sperm from entering and ensuring zygote formation.
Calcium
An essential ion in the cortical reaction during fertilization, it depolarizes the egg membrane, preventing polyspermy and signaling the completion of the egg's second meiotic division.
Membrane Potential
The voltage difference across a cell membrane due to the distribution of ions, crucial for processes like nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
Meiotic Division
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four genetically diverse haploid cells, essential for sexual reproduction.
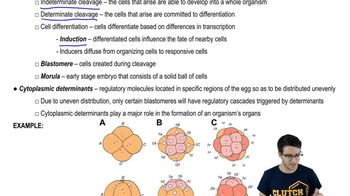
Cleavage
Rapid mitotic divisions of a zygote resulting in smaller cells called blastomeres, forming a solid ball of cells known as a morula, without increasing the overall size of the embryo.
Morula
An early-stage embryo consisting of a solid ball of cells formed by rapid mitotic divisions of a zygote, preceding the blastula stage.
Indeterminate Cleavage
A type of embryonic cleavage where each cell retains the potential to develop into a complete organism, allowing for the possibility of identical twins if cells separate.
Determinate Cleavage
Cells resulting from cleavage are committed to specific developmental fates, leading to specialized cell types and tissues, with no potential to form a complete organism independently.
Differentiation
The process by which a cell becomes specialized to perform a specific function, involving changes in gene expression and often influenced by external signals.
Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA, primarily mRNA, by the enzyme RNA polymerase, enabling gene expression.
Gene Expression
The process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize functional gene products, such as proteins, which ultimately determine the phenotype of an organism.
Induction
Differentiated cells influence the fate of nearby cells through chemical signals, guiding their development and specialization during embryogenesis.
Blastomeres
Cells formed during the early stages of embryonic development through rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote, leading to progressively smaller cells that will eventually differentiate into various tissues.
Cytoplasmic Determinants
Regulatory molecules in the egg's cytoplasm that are unevenly distributed during cleavage, leading to specialized cell development by triggering specific gene expression in resulting blastomeres.
Regulatory Molecules
Regulatory molecules are substances that control gene expression and cell differentiation during development by influencing transcription and signaling pathways.
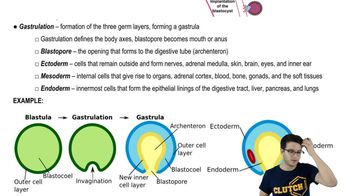
Blastulation
The process where a morula forms a hollow ball of cells called a blastula, with an inner fluid-filled cavity, marking a key stage in early embryonic development.
Blastocyst
A hollow, fluid-filled ball of cells formed during early mammalian embryonic development, consisting of an outer trophoblast layer and an inner cell mass that will develop into the embryo.
Blastula
A hollow sphere of cells formed during early embryonic development, characterized by a fluid-filled cavity, which in mammals is specifically termed a blastocyst.