Adaptive Immunity exam Flashcards
 Back
BackAdaptive Immunity exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
- Adaptive Immune SystemA part of the immune system that mounts specific defenses against pathogens through antigen recognition.
- B CellsLymphocytes that produce antibodies to bind antigens.
- T CellsLymphocytes that require antigen presentation via MHC proteins to become activated.
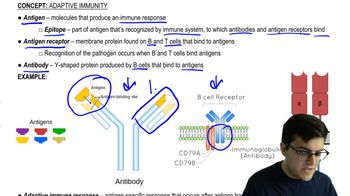
- AntigenA molecule that produces an immune response, often having multiple epitopes.
- AntibodiesY-shaped proteins produced by B cells that bind to antigens.
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)Proteins that present antigens on the cell surface for T cell recognition.
- Clonal ExpansionThe process by which activated B and T cells divide to form effector and memory cells.
- Effector CellsShort-lived cells that take immediate action against pathogens.
- Memory CellsLong-lived cells that remain in the body to respond quickly to future infections.
- Primary Immune ResponseThe initial response of the adaptive immune system to a new pathogen.
- Secondary Immune ResponseA faster and stronger immune response upon re-exposure to a previously encountered pathogen.
- VaccinationThe introduction of a vaccine to prime the immune system against future infections.
- Helper T CellsEffector T cells that assist in activating other immune cells by secreting cytokines.
- Cytotoxic T CellsEffector T cells that kill pathogen-infected cells.
- OpsonizationThe process by which antibodies enhance the phagocytosis of pathogens.
- AgglutinationThe clumping of pathogens due to antibodies binding multiple antigens.
- Passive ImmunityImmunity acquired by receiving antibodies from another individual.
- Active ImmunityImmunity developed through the production of antibodies in response to an infection or vaccination.
- Self-Nonself RecognitionThe ability of the immune system to distinguish between the body's own cells and foreign cells.
- Antigen PresentationThe display of antigens on the cell surface by MHC proteins for T cell recognition.
- CD4+ T CellsT cells that interact with MHC class II proteins and become helper T cells.
- CD8+ T CellsT cells that interact with MHC class I proteins and become cytotoxic T cells.
- Plasma CellsEffector B cells that produce and secrete large amounts of antibodies.
- Somatic HypermutationA process that allows B cells to fine-tune their antigen receptors for better binding.
- HIVA virus that infects and kills CD4+ T cells, leading to a weakened immune system.
- AIDSA condition resulting from HIV infection characterized by a severely weakened immune system.
- AllergiesAbnormal immune responses to non-threatening antigens, known as allergens.
- AutoimmunityAn immune response directed against the body's own cells and molecules.
- Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)Immune system cells found in the gut and respiratory tract that capture invading pathogens.