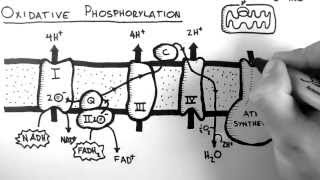
8. Respiration
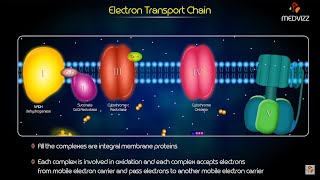
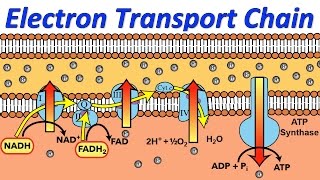
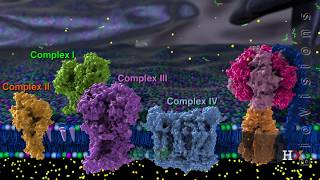
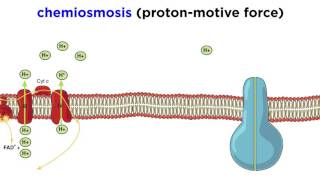
Electron Transport Chain
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
In the electron transport chain, the final electron acceptor is:
3091views24rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following events takes place in the electron transport chain?
5178views37rank - Multiple ChoiceMost of the electrons removed from glucose by cellular respiration are used for which of the following processes?1549views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following best describes the electron transport chain?1998views3rank
- Textbook Question
In mitochondria, exergonic redox reactions a. are the source of energy driving prokaryotic ATP synthesis. b. provide the energy that establishes the proton gradient. c. reduce carbon atoms to carbon dioxide. d. are coupled via phosphorylated intermediates to endergonic processes
1709views - Textbook Question
Cyanide binds to at least one molecule involved in producing ATP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the cyanide will be found within the a. mitochondria. b. ribosomes. c. peroxisomes. d. lysosomes.
3202views - Textbook Question
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of mitochondria, which of the following changes occurs? a. The pH of the matrix increases. b. ATP synthase pumps protons by active transport. c. The electrons gain free energy. d. NAD+ is oxidized.
2411views - Textbook Question
The poison cyanide binds to an electron carrier within the electron transport chain and blocks the movement of electrons. When this happens, glycolysis and the citric acid cycle soon grind to a halt as well. Why do you think these other two stages of cellular respiration stop? (Explain your answer.) a. They run out of ATP. b. Unused O2 interferes with cellular respiration. c. They run out of NAD+ and FAD. d. Electrons are no longer available.
4176views