13. Mendelian Genetics
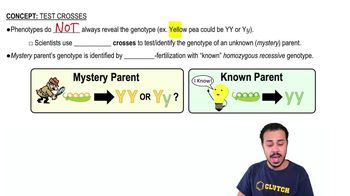
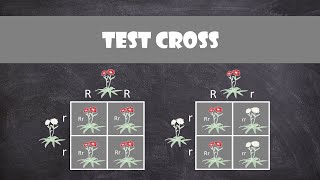
Test Crosses
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A single gene test cross is conducted to determine the genotype of a pea plant that shows the dominant phenotype for height (T = tall, t = short). If all offspring of the cross show the dominant phenotype, then the genotype of the unknown parent is _______.
2542views8rank2comments - Multiple Choice
You want to determine the pea color genotype of a pea plant with yellow peas. You conduct a test cross with your mystery pea plant. The test cross results in 50% of the offspring possessing yellow peas and 50% of the offspring possessing green peas. What is the genotype for pea color of the mystery parent?
1848views16rank - Multiple ChoiceWhat is indicated when a single-character testcross yields offspring that all have the dominant phenotype?956views
- Multiple ChoiceA gray-bodied, vestigial-winged fly is crossed with a black-bodied, normal-winged fly. The F1 progeny is testcrossed. Among the resulting offspring, __________ is a parental type, and __________ is a recombinant type.1153views1rank
- Textbook Question
Two black female mice are crossed with a brown male. In several litters, female I produced 9 black offspring and 7 brown; female II produced 57 black offspring. What deductions can you make about the inheritance of black and brown coat color in mice? What are the genotypes of the parents?
660views - Textbook QuestionIn flies, small wings are recessive to normal wings. If a cross between two flies produces 8 small-wing offspring and 28 normal-wing offspring, what are the most likely genotypes of the parents? (Use S to represent the normal-wing allele and s to represent the short-wing allele.)762views
- Textbook QuestionIn flies, small wings are recessive to normal wings. If a cross between two flies produces 8 small-wing offspring and 28 normal-wing offspring, what are the most likely genotypes of the parents? (Use S to represent the normal-wing allele and s to represent the short-wing allele.)435views
- Textbook Question
The smooth feathers on the back of the neck in pigeons can be reversed by a mutation to produce a 'crested' appearance in which feathers form a distinctive spike at the back of the head. A pigeon breeder examined offspring produced by a single pair of non-crested birds and recorded the following: 22 non-crested and 7 crested. She then made a series of crosses using offspring from the first cross. When she crossed two of the crested birds, all 20 of the offspring were crested. When she crossed a non-crested bird with a crested bird, 7 offspring were non-crested and 6 were crested. For these three crosses, provide genotypes for parents and offspring that are consistent with these results.
606views