22. Evolution of Populations
Genetic Variation
22. Evolution of Populations
Genetic Variation
Additional 21 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 24 of 24 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceThe human genome consists of approximately 3 billion base pairs. If humans typically differ from one another by about 3 million base pairs, what is the nucleotide variability of Homo sapiens?1337views
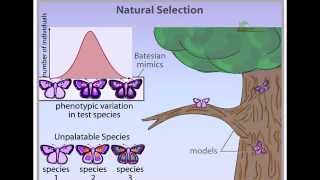
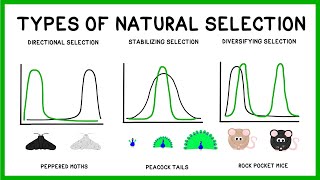
- Multiple ChoiceStabilizing selection __________.1047views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following mechanisms can form entirely new alleles?795views
- Multiple ChoiceSexual recombination includes the shuffling of chromosomes in __________ and fertilization.729views
- Textbook Question
Natural selection changes allele frequencies because some _________ survive and reproduce better than others. a. alleles b. loci c. species d. individuals
1245views - Textbook Question
The largest unit within which gene flow can readily occur is a a. population. b. species. c. genus. d. hybrid.
806views - Textbook Question
How do the phospholipids in archaea differ from those in other cells? a. They have tails made of unsaturated fatty acids instead of saturated fatty acids. b. They do not contain hydrocarbon chains. c. They have isoprenoid tails instead of fatty acid tails. d. They have two hydrocarbon chains instead of three hydrocarbon chains.
1153views - Textbook QuestionWhat two functional groups are bound to the central carbon of every free amino acid monomer? a. an R-group and a hydroxyl group b. an N—H group and a ═(C═O) group c. an amino group and a hydroxyl group d. an amino group and a carboxyl group1585views