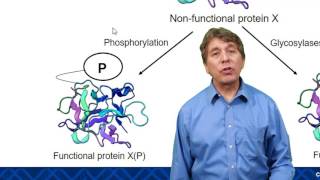
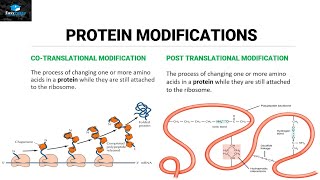
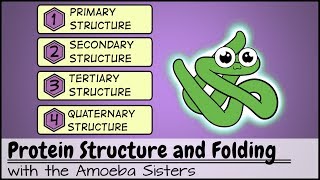
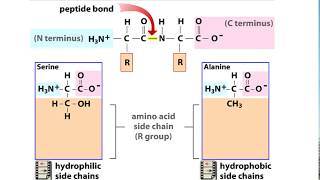
4. Biomolecules
Proteins
4. Biomolecules
Proteins
Showing 5 of 5 videos
Additional 13 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 16 of 16 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
The primary building blocks (monomers) of proteins are:
6871views66rank - Multiple Choice
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
11304views66rank - Multiple Choice
What term is used for an amino acid chain that has greater than 50 covalently linked amino acids?
5964views64rank - Multiple Choice
The specific amino acid sequence in a protein is its:
6238views57rank