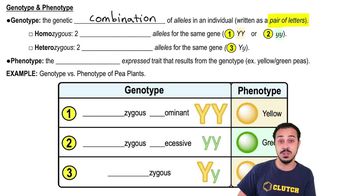
Textbook Question
This graph plots the rise and fall of pituitary and ovarian hormones during the human ovarian cycle. Identify each hormone (A–D) and the reproductive events with which each one is associated (P–S). For A–D, choose from estrogen, LH, FSH, and progesterone. For P–S, choose from ovulation, growth of follicle, menstruation, and development of corpus luteum. How would the right-hand side of this graph be altered if pregnancy occurred? What other hormone is responsible for triggering this change?
1803
views