Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Primase Function
Primase is an enzyme that synthesizes short RNA primers during DNA replication. These primers provide a starting point for DNA polymerase, which cannot initiate synthesis without a pre-existing strand. The RNA primers are complementary to the single-stranded DNA template, allowing for accurate replication.
Recommended video:
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. This process involves several key enzymes, including helicase, which unwinds the DNA, and DNA polymerase, which extends the new DNA strand. Primase plays a crucial role by laying down RNA primers to facilitate this process.
Recommended video:
Introduction to DNA Replication
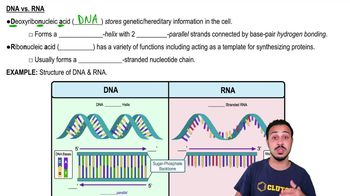
RNA vs. DNA
RNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) are both nucleic acids but differ in structure and function. RNA is typically single-stranded and contains ribose sugar, while DNA is double-stranded and contains deoxyribose sugar. The presence of uracil in RNA instead of thymine, which is found in DNA, is also a key distinction that affects their roles in cellular processes.
Recommended video: