Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
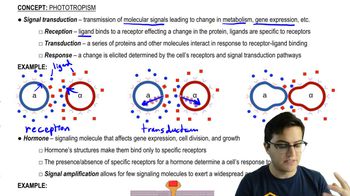
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction refers to the process by which a cell converts an external signal into a functional response. This involves a series of molecular events, often initiated by the binding of a signaling molecule (ligand) to a receptor on the cell surface, leading to changes in cellular activity. Understanding this concept is crucial for grasping how cells communicate and respond to their environment.
Recommended video:
Signal Transduction and Response
Signal Amplification
Signal amplification is a key aspect of signal transduction where a small initial signal can lead to a large cellular response. This is often achieved through a cascade of biochemical reactions, where each step activates multiple downstream molecules, thereby magnifying the effect of the original signal. This concept highlights the efficiency and sensitivity of cellular communication.
Recommended video:
Signal Modality Change
The concept of signal modality change refers to the transformation of a signal's physical form as it moves from the extracellular environment to the intracellular space. For instance, a chemical signal outside the cell may be converted into an electrical signal or a different biochemical form inside the cell, allowing for appropriate cellular responses. This transformation is essential for effective communication within the cell.
Recommended video: