Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Biology2h 40m
- 2. Chemistry3h 40m
- 3. Water1h 26m
- 4. Biomolecules2h 23m
- 5. Cell Components2h 26m
- 6. The Membrane2h 31m
- 7. Energy and Metabolism2h 0m
- 8. Respiration2h 40m
- 9. Photosynthesis2h 49m
- 10. Cell Signaling59m
- 11. Cell Division2h 47m
- 12. Meiosis2h 0m
- 13. Mendelian Genetics4h 41m
- Introduction to Mendel's Experiments7m
- Genotype vs. Phenotype17m
- Punnett Squares13m
- Mendel's Experiments26m
- Mendel's Laws18m
- Monohybrid Crosses16m
- Test Crosses14m
- Dihybrid Crosses20m
- Punnett Square Probability26m
- Incomplete Dominance vs. Codominance20m
- Epistasis7m
- Non-Mendelian Genetics12m
- Pedigrees6m
- Autosomal Inheritance21m
- Sex-Linked Inheritance43m
- X-Inactivation9m
- 14. DNA Synthesis2h 27m
- 15. Gene Expression3h 20m
- 16. Regulation of Expression3h 31m
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression13m
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons27m
- The Lac Operon21m
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon25m
- The Trp Operon20m
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon11m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation9m
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications16m
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control22m
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation28m
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation13m
- 17. Viruses37m
- 18. Biotechnology2h 58m
- 19. Genomics17m
- 20. Development1h 5m
- 21. Evolution3h 1m
- 22. Evolution of Populations3h 52m
- 23. Speciation1h 37m
- 24. History of Life on Earth2h 6m
- 25. Phylogeny2h 31m
- 26. Prokaryotes4h 59m
- 27. Protists1h 12m
- 28. Plants1h 22m
- 29. Fungi36m
- 30. Overview of Animals34m
- 31. Invertebrates1h 2m
- 32. Vertebrates50m
- 33. Plant Anatomy1h 3m
- 34. Vascular Plant Transport2m
- 35. Soil37m
- 36. Plant Reproduction47m
- 37. Plant Sensation and Response1h 9m
- 38. Animal Form and Function1h 19m
- 39. Digestive System10m
- 40. Circulatory System1h 57m
- 41. Immune System1h 12m
- 42. Osmoregulation and Excretion50m
- 43. Endocrine System4m
- 44. Animal Reproduction2m
- 45. Nervous System55m
- 46. Sensory Systems46m
- 47. Muscle Systems23m
- 48. Ecology3h 11m
- Introduction to Ecology20m
- Biogeography14m
- Earth's Climate Patterns50m
- Introduction to Terrestrial Biomes10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Near Equator13m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Temperate Regions10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Northern Regions15m
- Introduction to Aquatic Biomes27m
- Freshwater Aquatic Biomes14m
- Marine Aquatic Biomes13m
- 49. Animal Behavior28m
- 50. Population Ecology3h 41m
- Introduction to Population Ecology28m
- Population Sampling Methods23m
- Life History12m
- Population Demography17m
- Factors Limiting Population Growth14m
- Introduction to Population Growth Models22m
- Linear Population Growth6m
- Exponential Population Growth29m
- Logistic Population Growth32m
- r/K Selection10m
- The Human Population22m
- 51. Community Ecology2h 46m
- Introduction to Community Ecology2m
- Introduction to Community Interactions9m
- Community Interactions: Competition (-/-)38m
- Community Interactions: Exploitation (+/-)23m
- Community Interactions: Mutualism (+/+) & Commensalism (+/0)9m
- Community Structure35m
- Community Dynamics26m
- Geographic Impact on Communities21m
- 52. Ecosystems2h 36m
- 53. Conservation Biology24m
9. Photosynthesis
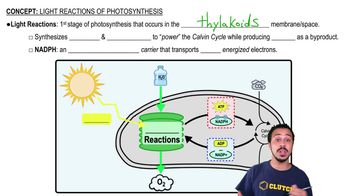
Light Reactions of Photosynthesis
Problem 6b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to a. substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis. b. oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration. c. carbon fixation. d. reduction of NADP+.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the process involved: Photophosphorylation is a process in photosynthesis where ATP is formed utilizing the energy of sunlight.
Understand the options: Compare photophosphorylation with each of the given options to find the most similar mechanism.
Analyze option b: Oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration also involves the generation of ATP through a chemiosmotic mechanism, similar to photophosphorylation.
Eliminate other options: Substrate-level phosphorylation involves direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP without a chemiosmotic mechanism, carbon fixation involves the incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules, and reduction of NADP+ is an electron transfer reaction, not directly involved in ATP synthesis.
Conclude that the correct answer is b. oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration, as both processes involve ATP synthesis through a chemiosmotic mechanism.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
49sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Photophosphorylation
Photophosphorylation is the process by which ATP is produced using the energy from light during photosynthesis. It occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, where light energy is converted into chemical energy, driving the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. This process is essential for providing the energy required for various cellular activities.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Prokaryote Metabolism
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a method of generating ATP directly in metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. In this process, a phosphate group is transferred from a phosphorylated substrate to ADP, forming ATP. This contrasts with oxidative phosphorylation, which relies on an electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Recommended video:
Guided course
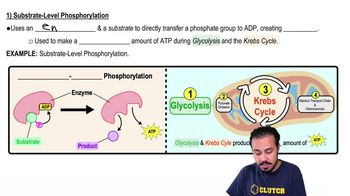
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the mitochondria, where ATP is produced through the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are transferred through a series of proteins, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. This process is crucial for energy production in aerobic organisms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
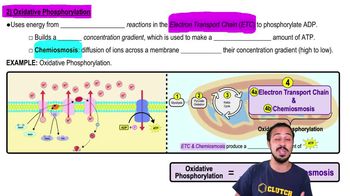
Oxidative Phosphorylation

 4:06m
4:06mWatch next
Master Light Reactions of Photosynthesis with a bite sized video explanation from Jason Amores Sumpter
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice