Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
PEP Carboxylase Function
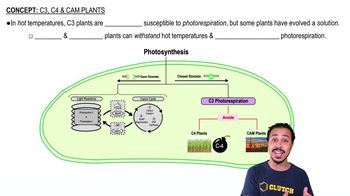
PEP carboxylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the fixation of carbon dioxide (CO2) into a four-carbon compound, typically oxaloacetate, in C4 and CAM plants. This process is crucial for these plants as it allows them to efficiently capture CO2 even in low concentrations, which is essential for photosynthesis in hot and arid environments.
Recommended video:
C4 and CAM Photosynthesis
C4 and CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) are two types of photosynthetic pathways that enable plants to minimize water loss and maximize CO2 fixation. C4 plants separate the initial CO2 fixation and the Calvin cycle spatially, while CAM plants do so temporally, fixing CO2 at night and conducting the Calvin cycle during the day, thus reducing transpiration.
Recommended video:
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle is the series of biochemical reactions that occur in the stroma of chloroplasts during photosynthesis, where CO2 is converted into glucose using ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions. In C4 and CAM plants, the initial fixation of CO2 by PEP carboxylase is a preparatory step that enhances the efficiency of the Calvin cycle under specific environmental conditions.
Recommended video: