Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Innate Immunity
Innate immunity is the first line of defense against pathogens, providing a rapid and non-specific response. It includes physical barriers like skin, as well as immune cells such as macrophages that recognize and eliminate invaders. This system does not require prior exposure to a pathogen, making it an essential component of the immune response.
Recommended video:
Adaptive Immunity
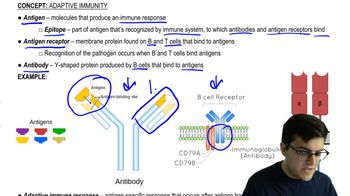
Adaptive immunity is a more specialized response that develops over time and is characterized by the ability to remember specific pathogens. It involves lymphocytes, such as B cells and T cells, which produce antibodies and mount a targeted attack against previously encountered pathogens. This system is crucial for long-term immunity but is not part of the innate immune response.
Recommended video:
Antibodies
Antibodies are proteins produced by B cells in response to specific antigens, which are foreign substances that provoke an immune response. They play a key role in adaptive immunity by binding to pathogens, neutralizing them, and marking them for destruction by other immune cells. Since antibodies are not part of the innate immune system, their presence indicates an adaptive immune response.
Recommended video:
Primary and Secondary Immunity