Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mitochondria Function
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through cellular respiration. This process is crucial for providing energy to various cellular functions. Cells that require more energy for their activities tend to have a higher number of mitochondria.
Recommended video:
Cellular Energy Demand
Different cell types have varying energy demands based on their functions. For instance, muscle cells, especially in athletes, require significant energy for contraction and endurance, leading to a higher concentration of mitochondria. In contrast, cells with lower energy needs, like some endocrine cells, may have fewer mitochondria.
Recommended video:
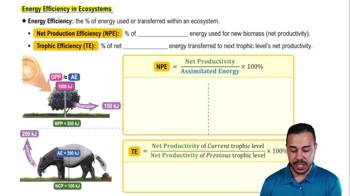
Energy Efficiency in Ecosystems
Cell Types and Their Functions
Understanding the specific functions of different cell types helps in predicting their mitochondrial content. For example, pancreatic cells are involved in digestion, ovarian cells in hormone production, and muscle cells in movement. The energy-intensive nature of muscle cells, particularly in athletes, suggests they would have the most mitochondria compared to the other cell types listed.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 4:19m
4:19m