Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alternation of Generations
Alternation of generations is a reproductive cycle in certain organisms, particularly plants and some algae, where there are two distinct multicellular stages: the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte. The gametophyte produces gametes through mitosis, while the sporophyte produces spores through meiosis, allowing for genetic diversity and adaptation.
Recommended video:
Laminaria Life Cycle: Alternation of Generations
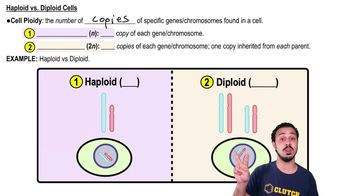
Haploid and Diploid Stages
In biological terms, haploid (n) refers to cells that contain a single set of chromosomes, while diploid (2n) cells contain two sets. In the context of alternation of generations, the haploid stage is typically represented by the gametophyte, which produces gametes, whereas the diploid stage is represented by the sporophyte, which produces spores.
Recommended video:
Haploid vs. Diploid Cells
Multicellularity in Life Cycles
Multicellularity refers to organisms composed of multiple cells that can differentiate into various types, allowing for complex structures and functions. In the alternation of generations, both the haploid and diploid stages can be multicellular, which is characteristic of many plants, enabling them to thrive in diverse environments and adapt to changing conditions.
Recommended video:
Protist Life Cycles Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:04m
1:04m