Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Biology2h 40m
- 2. Chemistry3h 40m
- 3. Water1h 26m
- 4. Biomolecules2h 23m
- 5. Cell Components2h 26m
- 6. The Membrane2h 31m
- 7. Energy and Metabolism2h 0m
- 8. Respiration2h 40m
- 9. Photosynthesis2h 49m
- 10. Cell Signaling59m
- 11. Cell Division2h 47m
- 12. Meiosis2h 0m
- 13. Mendelian Genetics4h 41m
- Introduction to Mendel's Experiments7m
- Genotype vs. Phenotype17m
- Punnett Squares13m
- Mendel's Experiments26m
- Mendel's Laws18m
- Monohybrid Crosses16m
- Test Crosses14m
- Dihybrid Crosses20m
- Punnett Square Probability26m
- Incomplete Dominance vs. Codominance20m
- Epistasis7m
- Non-Mendelian Genetics12m
- Pedigrees6m
- Autosomal Inheritance21m
- Sex-Linked Inheritance43m
- X-Inactivation9m
- 14. DNA Synthesis2h 27m
- 15. Gene Expression3h 20m
- 16. Regulation of Expression3h 31m
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression13m
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons27m
- The Lac Operon21m
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon25m
- The Trp Operon20m
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon11m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation9m
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications16m
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control22m
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation28m
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation13m
- 17. Viruses37m
- 18. Biotechnology2h 58m
- 19. Genomics17m
- 20. Development1h 5m
- 21. Evolution3h 1m
- 22. Evolution of Populations3h 52m
- 23. Speciation1h 37m
- 24. History of Life on Earth2h 6m
- 25. Phylogeny2h 31m
- 26. Prokaryotes4h 59m
- 27. Protists1h 12m
- 28. Plants1h 22m
- 29. Fungi36m
- 30. Overview of Animals34m
- 31. Invertebrates1h 2m
- 32. Vertebrates50m
- 33. Plant Anatomy1h 3m
- 34. Vascular Plant Transport2m
- 35. Soil37m
- 36. Plant Reproduction47m
- 37. Plant Sensation and Response1h 9m
- 38. Animal Form and Function1h 19m
- 39. Digestive System10m
- 40. Circulatory System1h 57m
- 41. Immune System1h 12m
- 42. Osmoregulation and Excretion50m
- 43. Endocrine System4m
- 44. Animal Reproduction2m
- 45. Nervous System55m
- 46. Sensory Systems46m
- 47. Muscle Systems23m
- 48. Ecology3h 11m
- Introduction to Ecology20m
- Biogeography14m
- Earth's Climate Patterns50m
- Introduction to Terrestrial Biomes10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Near Equator13m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Temperate Regions10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Northern Regions15m
- Introduction to Aquatic Biomes27m
- Freshwater Aquatic Biomes14m
- Marine Aquatic Biomes13m
- 49. Animal Behavior28m
- 50. Population Ecology3h 41m
- Introduction to Population Ecology28m
- Population Sampling Methods23m
- Life History12m
- Population Demography17m
- Factors Limiting Population Growth14m
- Introduction to Population Growth Models22m
- Linear Population Growth6m
- Exponential Population Growth29m
- Logistic Population Growth32m
- r/K Selection10m
- The Human Population22m
- 51. Community Ecology2h 46m
- Introduction to Community Ecology2m
- Introduction to Community Interactions9m
- Community Interactions: Competition (-/-)38m
- Community Interactions: Exploitation (+/-)23m
- Community Interactions: Mutualism (+/+) & Commensalism (+/0)9m
- Community Structure35m
- Community Dynamics26m
- Geographic Impact on Communities21m
- 52. Ecosystems2h 36m
- 53. Conservation Biology24m
41. Immune System
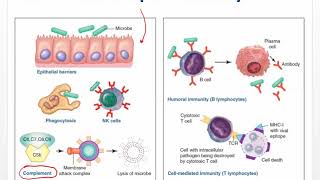
Adaptive Immunity
Problem 3a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWhich statement best describes the difference between responses of effector B cells (plasma cells) and those of cytotoxic T cells? a. B cells confer active immunity; cytotoxic T cells confer passive immunity. b. B cells respond the first time a pathogen is present; cytotoxic T cells respond subsequent times. c. B cells secrete antibodies against a pathogen; cytotoxic T cells kill pathogen-infected host cells. d. B cells carry out the cell-mediated response; cytotoxic T cells carry out the humoral response.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
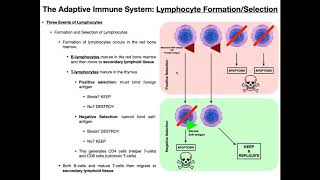
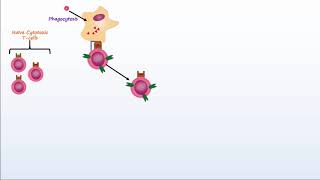
Understand the roles of B cells and cytotoxic T cells: B cells, also known as effector B cells or plasma cells, primarily function in the humoral immune response by producing antibodies that target specific antigens found on pathogens. Cytotoxic T cells, on the other hand, are involved in the cell-mediated immune response, where they directly kill cells that are infected with viruses or are otherwise dysfunctional.
Analyze the options: Option a suggests a difference in the type of immunity conferred by B cells and cytotoxic T cells, which is incorrect as both are part of active immunity. Option b is incorrect as it misrepresents the primary and secondary immune responses; both B cells and cytotoxic T cells can be involved in primary and secondary responses.
Focus on the correct functions: Option c correctly identifies that B cells secrete antibodies that bind to pathogens, whereas cytotoxic T cells kill pathogen-infected host cells directly. This statement accurately reflects the distinct roles each plays in the immune system.
Eliminate incorrect options: Option d incorrectly swaps the roles of B cells and cytotoxic T cells, stating that B cells are involved in cell-mediated responses and cytotoxic T cells in humoral responses, which is the opposite of their actual functions.
Select the correct answer: Based on the analysis, the correct answer is option c, as it accurately describes the functional differences between B cells and cytotoxic T cells in the immune system.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
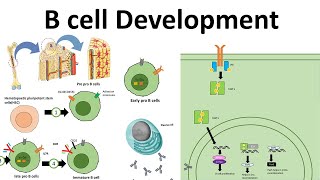
B Cells and Antibody Production
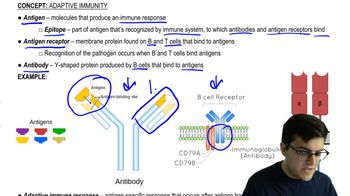
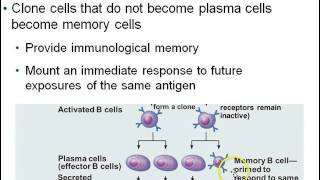
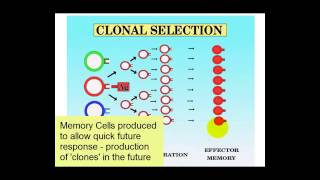
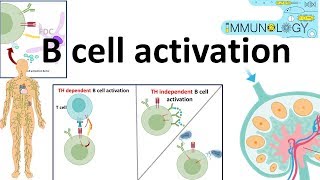
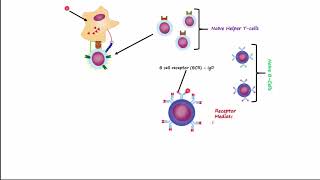
B cells, or plasma cells, are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune response by producing antibodies. These antibodies are specific proteins that bind to antigens on pathogens, neutralizing them or marking them for destruction by other immune cells. This process is part of the humoral immune response, which is essential for targeting extracellular pathogens.
Recommended video:
Guided course

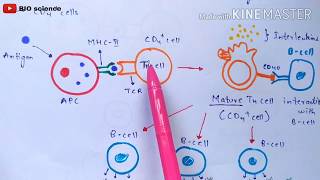
Helper T Cells and B Cells
Cytotoxic T Cells and Cell-Mediated Immunity
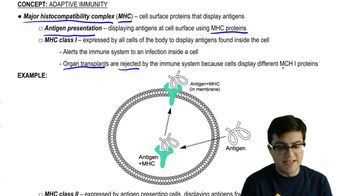
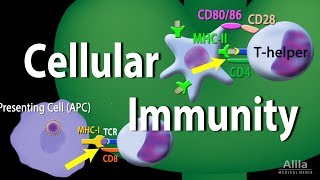
Cytotoxic T cells, also known as CD8+ T cells, are responsible for directly killing infected host cells, particularly those infected by viruses or transformed by cancer. They recognize infected cells through specific antigens presented on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. This function is a key component of the cell-mediated immune response, which is vital for controlling intracellular pathogens.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Antigen Presentation and Cytotoxic T Cells
Active vs. Passive Immunity
Active immunity occurs when the immune system is exposed to a pathogen and produces its own antibodies, leading to long-lasting protection. In contrast, passive immunity involves the transfer of antibodies from one individual to another, providing immediate but temporary protection. Understanding this distinction is important for interpreting the roles of B cells and T cells in the immune response.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Passive vs. Active Transport

 5:50m
5:50mWatch next
Master Adaptive Immune Response with a bite sized video explanation from Jason Amores Sumpter
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice