Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Inflammation
Inflammation is a biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. It involves the activation of immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators, leading to increased blood flow and the accumulation of immune cells at the site of injury or infection. This process is characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain, which serve as signals for the body to initiate healing.
Role of Inflammation in Protection
Inflammation plays a crucial protective role by isolating and eliminating pathogens and damaged cells. The increased blood flow brings immune cells to the affected area, where they can attack invaders and clear debris. Additionally, inflammatory mediators can enhance the permeability of blood vessels, allowing more immune components to reach the site of injury, thus facilitating the healing process and preventing the spread of infection.
Recommended video:
2) mRNA Protection in the Cytoplasm
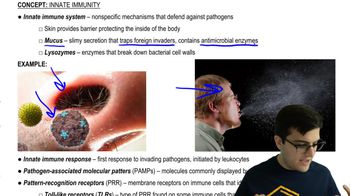
Innate Immune Response
The innate immune response is the body's first line of defense against pathogens, characterized by its rapid and non-specific action. Inflammation is a key component of this response, as it is activated immediately upon detection of harmful agents. Unlike the adaptive immune response, which develops over time and targets specific pathogens, the innate response, including inflammation, provides immediate protection and helps to contain infections until the adaptive immune system can take over.
Recommended video: