Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, primarily in the form of glucose. It involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions, which capture energy from sunlight, and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle), which use that energy to synthesize sugars from carbon dioxide.
Recommended video:
Pigments of Photosynthesis
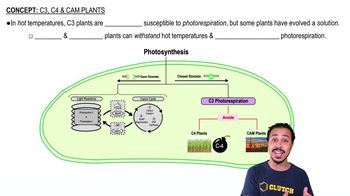
C4 and CAM Pathways
C4 and CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) are two adaptations that some plants use to efficiently fix carbon dioxide in environments with high temperatures and low water availability. C4 plants separate the initial carbon fixation and the Calvin cycle spatially, while CAM plants separate these processes temporally, fixing carbon at night and conducting the Calvin cycle during the day.
Recommended video:
Rubisco
Rubisco, or ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, is the enzyme responsible for fixing carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle. In C4 and CAM plants, the initial carbon fixation is carried out by other enzymes, allowing these plants to minimize photorespiration and enhance efficiency in carbon fixation under stress conditions.
Recommended video:
3 Phases of the Calvin Cycle (C3 Pathway)