Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Photorespiration
Photorespiration is a metabolic process in plants that occurs when the enzyme RuBisCO fixes oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, leading to a wasteful pathway that reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis. This process is more likely to happen under conditions of high temperature and low carbon dioxide availability, which can occur during hot and dry weather.
Recommended video:
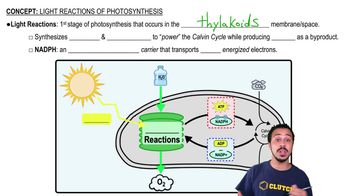
Light-Independent Reactions
The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, are a series of biochemical reactions that occur in the stroma of chloroplasts, where carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules. While these reactions primarily utilize carbon dioxide, photorespiration can occur when oxygen is mistakenly incorporated, leading to a decrease in the overall yield of glucose.
Recommended video:
Light Reactions of Photosynthesis
Environmental Conditions Affecting Photosynthesis
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide concentration significantly influence the rate of photosynthesis and the occurrence of photorespiration. Under hot and dry conditions, stomata close to conserve water, which can lead to increased oxygen levels inside the leaf and a higher likelihood of photorespiration occurring.
Recommended video:
Environmental Tonicity Affects Cells
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution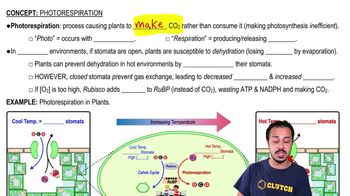


 14:32m
14:32m