Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Fluid Mosaic Model
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of cell membranes as a dynamic and flexible arrangement of various components, including lipids and proteins. In this model, the lipid bilayer acts as a fluid medium in which proteins are embedded, allowing for movement and interaction. This model emphasizes that membranes are not static but rather exhibit fluidity, enabling cellular processes such as signaling and transport.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Population Growth Models
Lipid Bilayer
The lipid bilayer is a fundamental structure of cell membranes, composed of two layers of phospholipids. Each phospholipid molecule has a hydrophilic (water-attracting) 'head' and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) 'tails.' This arrangement creates a semi-permeable barrier that separates the internal environment of the cell from the external surroundings, allowing selective passage of substances and maintaining homeostasis.
Recommended video:
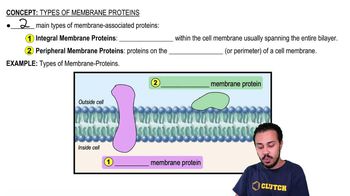
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are integral or peripheral proteins that perform various functions within the cell membrane. They can be embedded within the lipid bilayer or attached to its surface, playing roles in transport, signaling, and structural support. The orientation and distribution of these proteins are crucial for their function, as they interact with both the extracellular environment and the cytoplasm, facilitating communication and material exchange.
Recommended video:
Types of Membrane Proteins
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 6:04m
6:04m