Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mitochondrial Function
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell because they generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell, through cellular respiration. This process involves converting nutrients into energy, which is essential for various cellular functions and overall metabolism.
Recommended video:
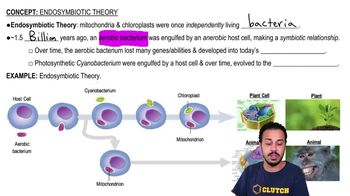
Endosymbiotic Theory
The endosymbiotic theory posits that mitochondria originated from free-living prokaryotic organisms that were engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells. This symbiotic relationship allowed the host cell to utilize the energy produced by the engulfed prokaryotes, leading to the evolution of complex eukaryotic cells.
Recommended video:
Mitochondrial Independence
While mitochondria are integral to eukaryotic cells, they possess their own DNA and can replicate independently of the cell's nuclear DNA. However, they are not fully independent; they rely on the host cell for certain proteins and other components necessary for their function and maintenance.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 4:19m
4:19m