Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Wolff's Law
Wolff's Law states that bone in a healthy person or animal will adapt to the loads under which it is placed. This means that the shape and density of bone are influenced by the mechanical stresses it experiences, leading to changes in bone structure to better support those stresses.
Recommended video:
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is a continuous process where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue. This process is influenced by various factors, including mechanical stress, hormones, and nutritional status, and is essential for maintaining bone strength and integrity throughout life.
Recommended video:
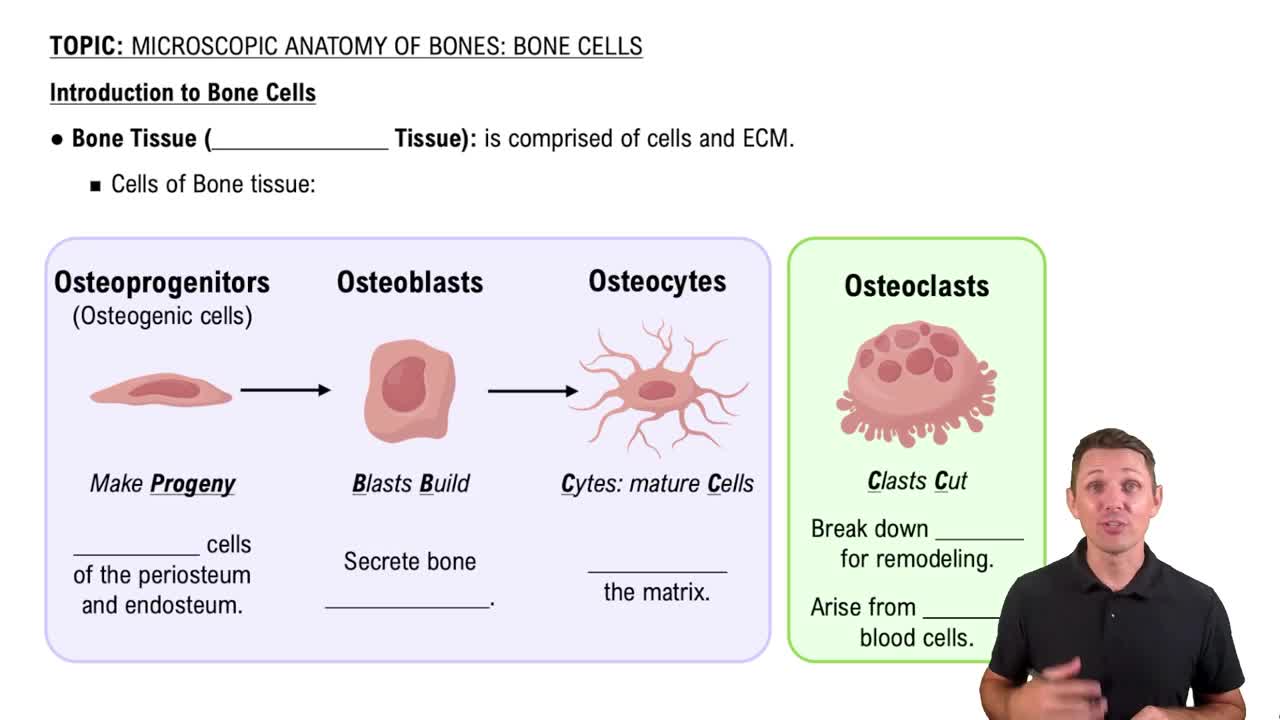
Introduction to Bone Cells
Mechanical Stress
Mechanical stress refers to the forces applied to a bone, which can result from activities such as weight-bearing exercises or physical labor. These stresses stimulate bone remodeling and adaptation, leading to changes in bone density and structure in response to the demands placed on it.
Recommended video:
Internal Regulation - The Myogenic Mechanism
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance