In which direction would you be unable to move your right eye if your right abducens nerve were damaged?
Fill in the blanks: In an olfactory neuron, the binding of a(n) ______to its membrane receptor triggers a(n)_______potential in the axons of the______nerve.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Olfactory Receptors

Action Potential
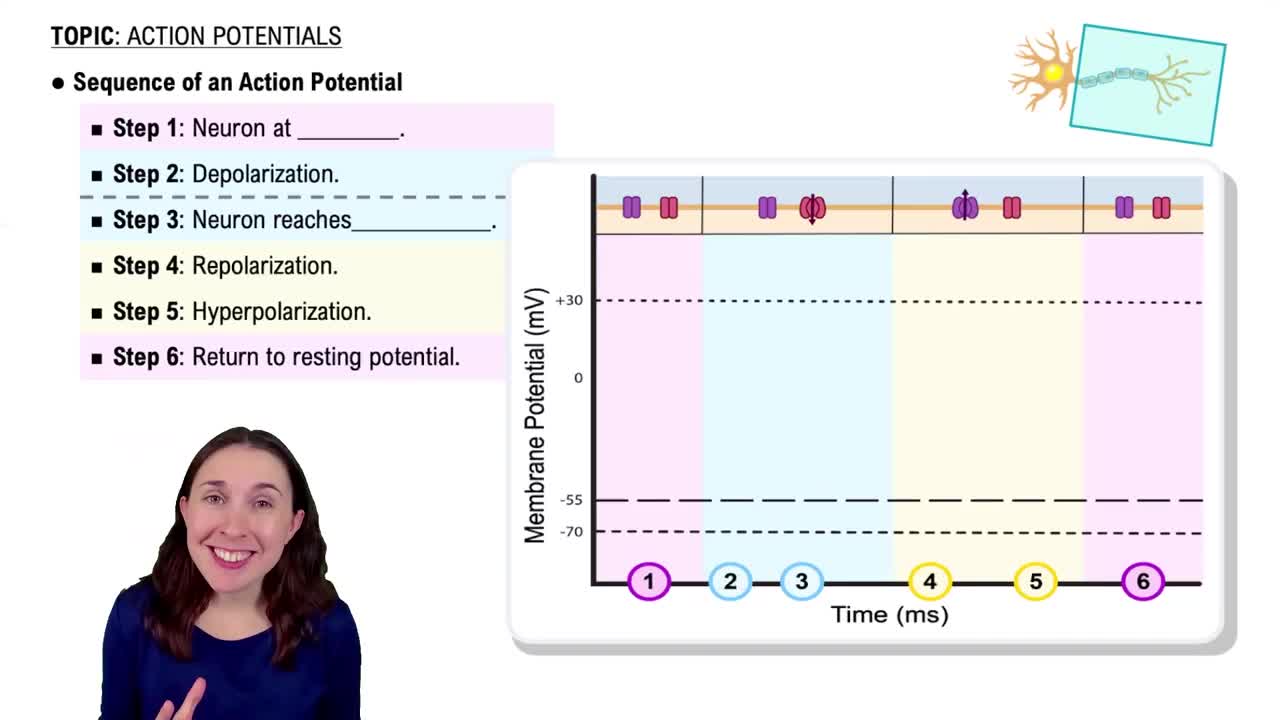
Olfactory Nerve
Your friend tells you that she has just been diagnosed with myopia, and she wonders if staring at her computer screen too much might have caused her problem. What do you tell her?
Stimuli from the inner ear regarding head movement and position are sent to all of the following except the:
a. vestibular nuclei.
b. oculomotor nucleus.
c. parietal lobe.
d. cerebellum.
e. trigeminal nucleus.
If a patient suffers visual impairment only in one eye, why must the damage be located in the visual pathway prior to the optic chiasma?
If severe congestion from a cold prevented your pharyngotympanic tube from opening, what could happen to your tympanic membrane? Explain your answer.
The primary olfactory cortex is located in the:
a. frontal lobe.
b. occipital lobe.
c. parietal lobe.
d. temporal lobe.
