Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
c. The Na+/K+ pumps and gated channels maintain the Na+ and K+ gradients necessary for action potentials to occur.
 Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition
Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition Ch. 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
Ch. 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Problem 11.10a
Problem 11.10a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

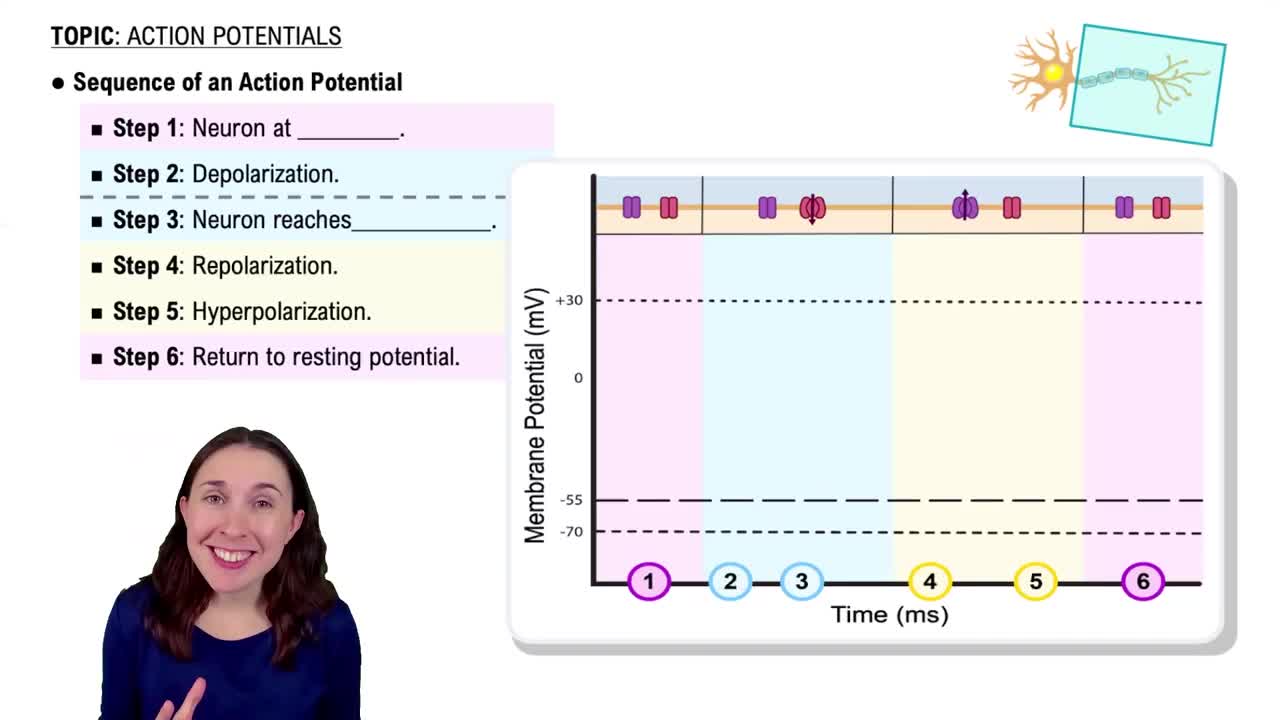

Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
c. The Na+/K+ pumps and gated channels maintain the Na+ and K+ gradients necessary for action potentials to occur.
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
d. A depolarization is a change in membrane potential that makes the potential less negative.
Describe the three components of the neuromuscular junction.
A drug that blocks Na+ channels in neurons does so not only in the axon but also in the dendrites and cell body. What overall effect would this have on action potential generation?
The drug neostigmine blocks the actions of acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft. What effect would this have on synaptic transmission? What effects might you expect to see as a result of this drug?
Which of the following is not a method by which the effects of neurotransmitters are terminated?
a. Reuptake into the presynaptic neuron
b. Diffusion away from the synaptic cleft and uptake by glial cells
c. Movement back to the cell body by retrograde axonal transport
d. Degradation by enzymes in the synaptic cleft