Explain how an action potential is propagated down an axon in continuous conduction. Why is saltatory conduction faster than continuous conduction?
 Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition
Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition Ch. 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
Ch. 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Problem 11.6a
Problem 11.6aExplain what would happen if depolarization of the trigger zone led to a negative feedback loop instead of a positive one. (Connects to Chapter 1)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Depolarization
Feedback Loops

Trigger Zone
Albert, the patient in question 3, takes the drug lithium, which reduces the permeability of the neuronal axolemma to Na+ (that is, it allows fewer Na+ to enter the axon). Predict the effect this would normally have on his neuronal action potentials. Do you think this drug would be beneficial or harmful, considering his condition?
Predict the effect that tetrodotoxin would have on Albert's muscle fiber action potentials (see question 3). Would it affect end-plate potentials at the motor end plate? Why or why not? (Connects to Chapter 10)
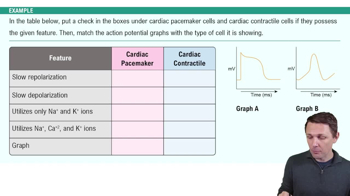
Fill in the blanks: The______is the period of time during which it is impossible to stimulate a neuron to have an action potential, whereas the______ is the period of time during which a larger-than-normal stimulus is required to elicit an action potential.
Which of the following statements best describes saltatory conduction?
a. Every section of the axolemma must be depolarized and triggered to generate an action potential.
b. The internodes must generate action potentials.
c. The dendrites and cell bodies propagate EPSPs toward the trigger zone.
d. Only the nodes of Ranvier must generate action potentials.
Identify the following as properties of electrical synapses (ES), chemical synapses (CS), or both (B).
a. ______The plasma membranes of presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons are joined by gap junctions.
b. ______Transmission is unidirectional and delayed.
c. ______A presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron are involved.
d. ______The use of neurotransmitters packaged into synaptic vesicles is required.
e. ______Transmission is nearly instantaneous and bidirectional.