Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement if false, correct it to make a true statement.
b. Postsynaptic potentials may summate by spatial summation in which multiple neurons fire onto a single postsynaptic neuron.
 Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition
Erin C. Amerman 2nd Edition Ch. 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
Ch. 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Problem 11.2a
Problem 11.2a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


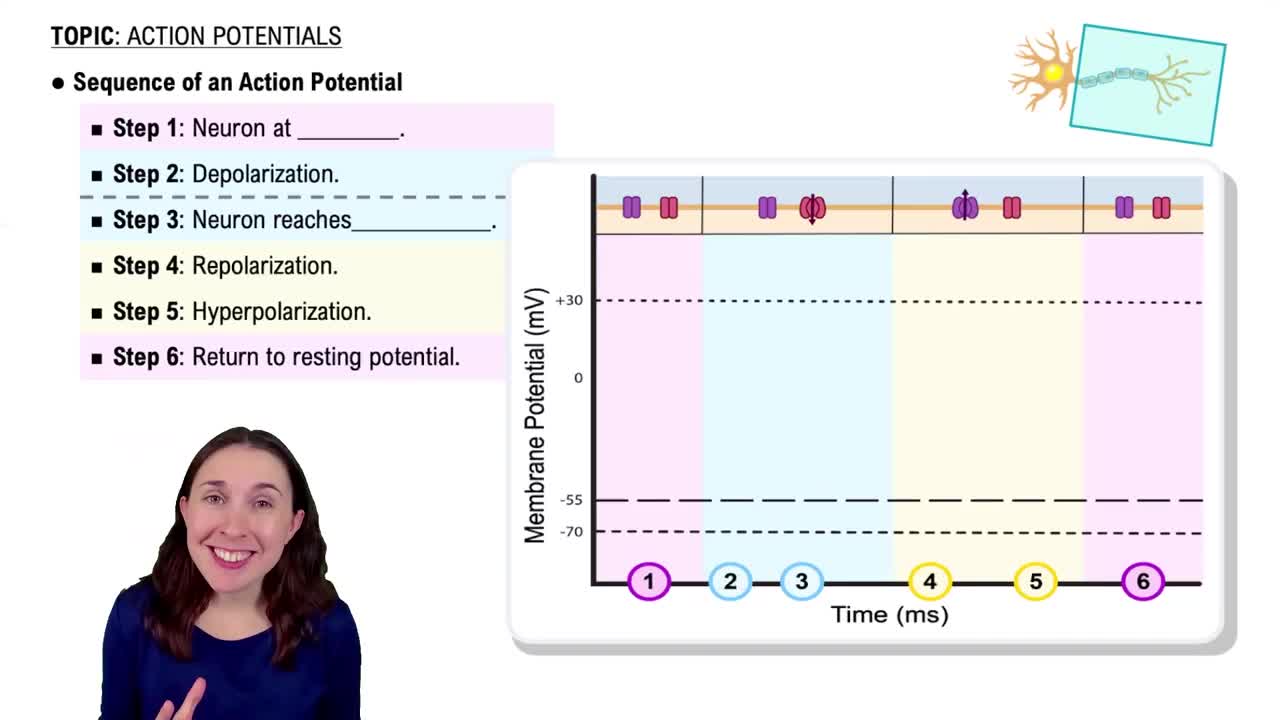
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement if false, correct it to make a true statement.
b. Postsynaptic potentials may summate by spatial summation in which multiple neurons fire onto a single postsynaptic neuron.
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement if false, correct it to make a true statement.
c. An inhibitory postsynaptic potential causes the membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron to approach threshold.
What would happen if the drug blocked K+ channels instead?
Albert accidentally ingests the poison tetrodotoxin from the pufferfish, which you know blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels. Predict the symptoms Albert will experience from this poisoning.
Explain how an action potential is propagated down an axon in continuous conduction. Why is saltatory conduction faster than continuous conduction?
Albert, the patient in question 3, takes the drug lithium, which reduces the permeability of the neuronal axolemma to Na+ (that is, it allows fewer Na+ to enter the axon). Predict the effect this would normally have on his neuronal action potentials. Do you think this drug would be beneficial or harmful, considering his condition?