Sympathetic Nervous System definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSympathetic Nervous System definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
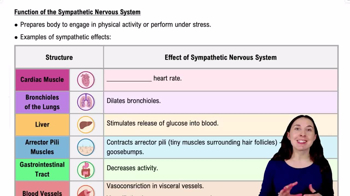
- Sympathetic Nervous SystemActivates during stress, increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and airflow, while decreasing gastrointestinal activity.
- Fight or Flight ResponseA physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival.
- Preganglionic FiberThe short nerve fiber that originates in the spinal cord and synapses in a ganglion.
- Postganglionic FiberThe long nerve fiber that extends from a ganglion to the target organ.
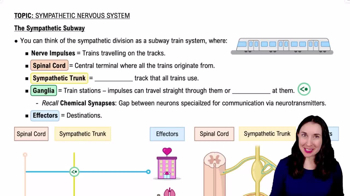
- Sympathetic TrunkA bundle of nerve fibers running parallel to the spinal cord, involved in transmitting nerve impulses.
- GangliaStructures acting as relay points where nerve impulses can synapse or pass through.
- Splanchnic NervesNerves that bypass the sympathetic trunk to synapse in collateral ganglia near abdominal organs.
- Adrenal MedullaPart of the sympathetic nervous system, secreting adrenaline and noradrenaline for the fight or flight response.
- VasoconstrictionThe narrowing of blood vessels, reducing blood flow to certain areas like the stomach or intestines.
- VasodilationThe widening of blood vessels, increasing blood flow to skeletal muscles during stress.
- Arrector Pili MusclesTiny muscles around hair follicles that contract to cause goosebumps.
- Dual InnervationMost organs receive nerve fibers from both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
- White Ramus CommunicansCarries preganglionic fibers from the spinal nerve to the sympathetic ganglia.
- Gray Ramus CommunicansCarries postganglionic fibers from the ganglia back to the spinal nerve.
- Collateral GanglionGanglia located closer to effector organs where splanchnic nerves synapse.