Structural Class: Synovial Joints definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackStructural Class: Synovial Joints definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
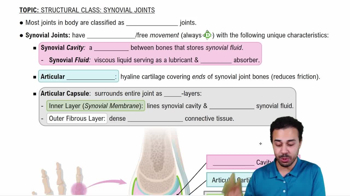
- Synovial JointsMost common joint type in the human body, allowing free movement and classified as diarthroses.
- DiarthrosesFunctional classification of joints that allow for dynamic and free movement.
- Synovial CavitySpace between bones in a synovial joint, storing synovial fluid for lubrication and shock absorption.
- Synovial FluidViscous liquid in synovial joints, acting as a lubricant and shock absorber.
- Articular CartilageHyaline cartilage covering bone ends in synovial joints, reducing friction and absorbing shock.
- Articular CapsuleStructure surrounding synovial joints, consisting of an inner synovial membrane and an outer fibrous layer.
- Synovial MembraneInner layer of the articular capsule, producing synovial fluid.
- Fibrous LayerOuter layer of the articular capsule, made of dense irregular connective tissue for stability.
- Weeping LubricationProcess where synovial fluid is expelled and reabsorbed by articular cartilage during joint movement.
- BursaeFluid-filled sacs in some synovial joints, reducing friction between tissues.
- Tendon SheathsElongated bursae wrapping around tendons to reduce friction.
- Fatty PadsAdipose tissue in joints like the knee, providing extra cushioning.
- Articular DiscsFibrocartilage structures dividing synovial cavities, acting as shock absorbers.
- MenisciFibrocartilage discs in joints like the knee, providing stability and shock absorption.
- LigamentsStructures reinforcing synovial joints, enhancing stability.