Stratified Epithelial Tissues definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackStratified Epithelial Tissues definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
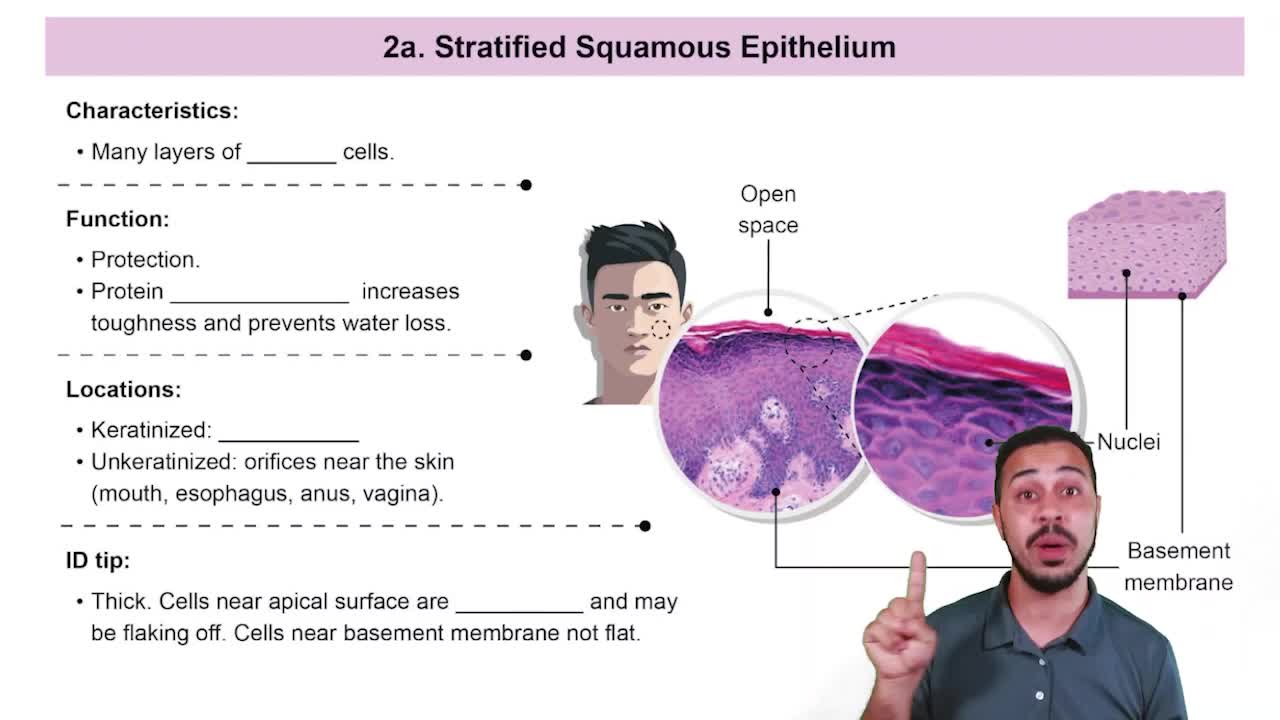
- Stratified EpitheliumTissue with multiple layers of cells, providing protection and not all cells contact the basement membrane.
- Squamous CellsFlat, squished cells found at the apical surface of stratified squamous epithelium, providing protection.
- KeratinA tough, waterproof protein found in keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, enhancing protection.
- Transitional EpitheliumStratified tissue with cells that change shape from cuboidal to squamous, found in the urinary system.
- Cuboidal CellsCube-shaped cells found at the apical surface of stratified cuboidal epithelium, aiding in protection and secretion.
- Columnar CellsTall, narrow cells found at the apical surface of stratified columnar epithelium, providing protection and limited absorption.
- Basement MembraneA thin layer separating epithelial tissue from underlying connective tissue, providing support.
- Apical SurfaceThe topmost layer of cells in epithelial tissue, exposed to the external environment or internal space.
- Keratinized EpitheliumStratified squamous epithelium containing keratin, found in dry areas like skin.
- Unkeratinized EpitheliumStratified squamous epithelium without keratin, found in moist areas like the mouth and esophagus.
- UrotheliumAnother term for transitional epithelium, specifically found in the urinary system.
- Goblet CellsCells that may be present in stratified columnar epithelium, secreting mucus.
- ElasticityThe ability of transitional epithelium to stretch and return to its original shape, crucial for bladder function.
- DesmosomesStructures that hold epithelial cells together, maintaining tissue integrity during stretching.
- Tight JunctionsCell connections in epithelial tissue that prevent leakage of molecules between cells.