Steps of Muscle Contraction definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSteps of Muscle Contraction definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
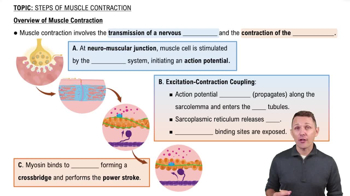
- Neuromuscular JunctionThe site where a motor neuron communicates with a muscle fiber, initiating muscle contraction.
- AcetylcholineA neurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction to trigger muscle contraction.
- SarcolemmaThe cell membrane of a muscle fiber that conducts action potentials.
- T-tubulesInvaginations of the sarcolemma that help propagate action potentials into the muscle fiber.
- Sarcoplasmic ReticulumA specialized endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells that stores and releases calcium ions.
- Calcium IonsIons released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum that bind to troponin to initiate contraction.
- TroponinA protein that binds calcium ions, causing tropomyosin to expose myosin binding sites on actin.
- TropomyosinA protein that blocks myosin binding sites on actin filaments in resting muscle.
- Cross-bridgeThe connection formed when myosin heads bind to actin filaments during muscle contraction.
- Power StrokeThe action of myosin pulling actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere.
- ATP HydrolysisThe process of breaking down ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate, providing energy for muscle contraction.
- DepolarizationA change in cell membrane potential that makes the inside of the cell more positive.
- RepolarizationThe process of restoring the resting membrane potential after depolarization.
- AcetylcholinesteraseAn enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft, ending muscle contraction.
- MyofibrilA basic rod-like unit of a muscle cell, composed of repeating sarcomeres.