Small Intestine definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSmall Intestine definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
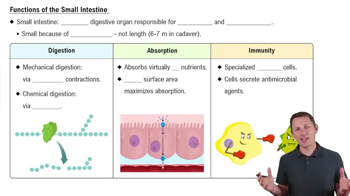
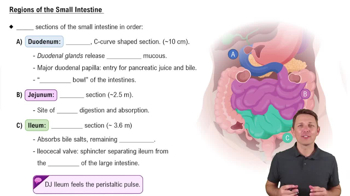
- DuodenumThe first section of the small intestine, mixing chyme with bile and pancreatic juice, and releasing alkaline mucus.
- JejunumThe middle section of the small intestine, primarily responsible for nutrient absorption through microvilli.
- IleumThe longest section of the small intestine, absorbing bile salts and remaining nutrients.
- PeristalsisA wave of muscle contraction that moves chyme through the gastrointestinal tract.
- SegmentationNon-adjacent muscle contractions in the small intestine aiding in mechanical digestion and mixing.
- MicrovilliMembrane projections on enterocytes, increasing surface area for absorption and containing brush border enzymes.
- EnterocytesSimple columnar cells specialized for absorption in the small intestine, lining the villi.
- Goblet cellsCells in the intestinal mucosa that secrete mucus to lubricate the alimentary canal.
- Peyer's patchesAggregated lymphoid nodules in the ileum protecting against pathogens from the large intestine.
- Paneth cellsCells at the base of intestinal crypts secreting antimicrobial agents like lysozyme and defensins.
- Brush borderThe microvilli-covered surface of enterocytes, containing enzymes for the final steps of digestion.
- Circular foldsFolds of the mucosa and submucosa in the small intestine, increasing surface area and slowing chyme flow.
- Ileocecal valveThe sphincter separating the ileum from the cecum of the large intestine, controlling chyme passage.
- ChymeThe semi-fluid mass of partly digested food that moves from the stomach to the small intestine.
- LactealA lymph vessel within the villi of the small intestine, absorbing lipids from digested food.