Rods, Cones, and Light definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackRods, Cones, and Light definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
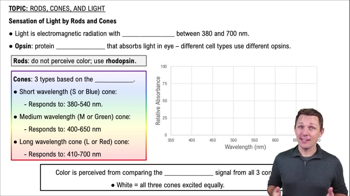
- OpsinA protein pigment in the eye that absorbs light, enabling the perception of different wavelengths.
- RhodopsinThe opsin used by rods, absorbing light best at 500 nanometers, crucial for grayscale vision.
- RodsPhotoreceptor cells in the eye that perceive light in grayscale using rhodopsin.
- ConesPhotoreceptor cells in the eye that perceive color using three types of opsins.
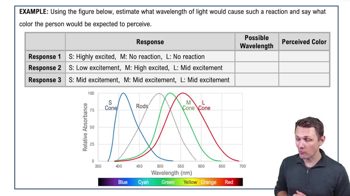
- Short Wavelength ConeAlso known as the S or blue cone, it absorbs light best at 420 nanometers.
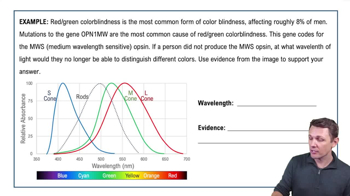
- Medium Wavelength ConeAlso known as the M or green cone, it absorbs light best around 535 nanometers.
- Long Wavelength ConeAlso known as the L or red cone, it absorbs light best at 565 nanometers.
- Color PerceptionArises from comparing the relative signals received from all three types of cones.
- Electromagnetic RadiationLight is a form of this, with wavelengths between 387 and 700 nanometers.
- WavelengthThe distance between successive peaks of a wave, crucial for determining light color.
- Relative AbsorbanceA measure of how much light a photoreceptor absorbs at a given wavelength.
- Color BlindnessA condition where certain colors cannot be distinguished, often due to cone deficiencies.
- Graph InterpretationUnderstanding graphs of wavelength versus absorbance is key to grasping color vision.
- Signal PatternThe unique combination of signals from cones that the brain interprets as a specific color.
- White PerceptionOccurs when all three cones are equally excited by a bright mix of wavelengths.